Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a database server for storing and retrieving data.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have the following details before configuring Microsoft SQL Server as a source:
- Hostname or IP address of the database
- Port
- Outbound port (1433 is the default port) open in your AWS or Azure security group
- Ensure that the database version is Microsoft SQL Server version 2012 or later
User Impersonation
The Microsoft SQL Server username provided in the source configuration is the default username that is used for running queries. When queries are run against Microsoft SQL Server in Dremio Cloud, users use the privileges associated with the Microsoft SQL Server username and run queries under that username.
You can change this default in Dremio Cloud by enabling user impersonation in the Advanced Options, which allows users to run queries under their own usernames and restricts their access. For example, user_1 can run queries as user_1 rather than sqlsvr_svc. Before enabling user impersonation, some setup is required in Microsoft SQL Server to allow one user to impersonate another user because the username of the user in Dremio Cloud must be the same as their username in Microsoft SQL Server and the user must be able to connect through the Microsoft SQL Server username.
To set up user impersonation, follow these steps:
-
Ensure the user's username in Microsoft SQL Server matches their username in Dremio Cloud. If the usernames do not match, modify one of the usernames or create a new user account with a matching username.
-
Run a GRANT IMPERSONATE command in Microsoft SQL Server to allow the user to connect through their Microsoft SQL Server username:
GRANT IMPERSONATE ON USER::testuser1 TO proxyuser;
In this example, the user can log in as testuser1 in Dremio Cloud and in Microsoft SQL Server, and they can connect through the proxyuser. The proxyuser is the Microsoft SQL Server username provided in the source configuration.
-
Log in to Dremio Cloud as a member of the ADMIN role.
-
Follow the steps for Configuring Microsoft SQL Server as a Source using the Microsoft SQL Server username
proxyuserand enable User Impersonation in the Advanced Options. -
Grant source privileges to the user.
Now that you have enabled user impersonation, a user who logs in to Dremio Cloud with their username can access the Microsoft SQL Server source and its datasets according to their privileges. The user can also run queries against Microsoft SQL Server under their username.
Configuring Microsoft SQL Server as a Source
Perform these steps to configure Microsoft SQL Server as a source:
-
On the Datasets page, you can see a truncated list of Sources at the bottom-left of the page. Click Add Source.
Alternatively, click Databases. The page displays all database sources. Click the Add database button at the top-right of that page.
-
In the Add Data Source dialog, click Microsoft SQL Server.
The following section describes the source configuration tabs.
noteSources containing a large number of files or tables may take longer to be added. During this time, the source name is grayed out and shows a spinner icon, indicating the source is being added. Once complete, the source becomes accessible.
General
The General tab contains the required fields to create a Microsoft SQL Server source.
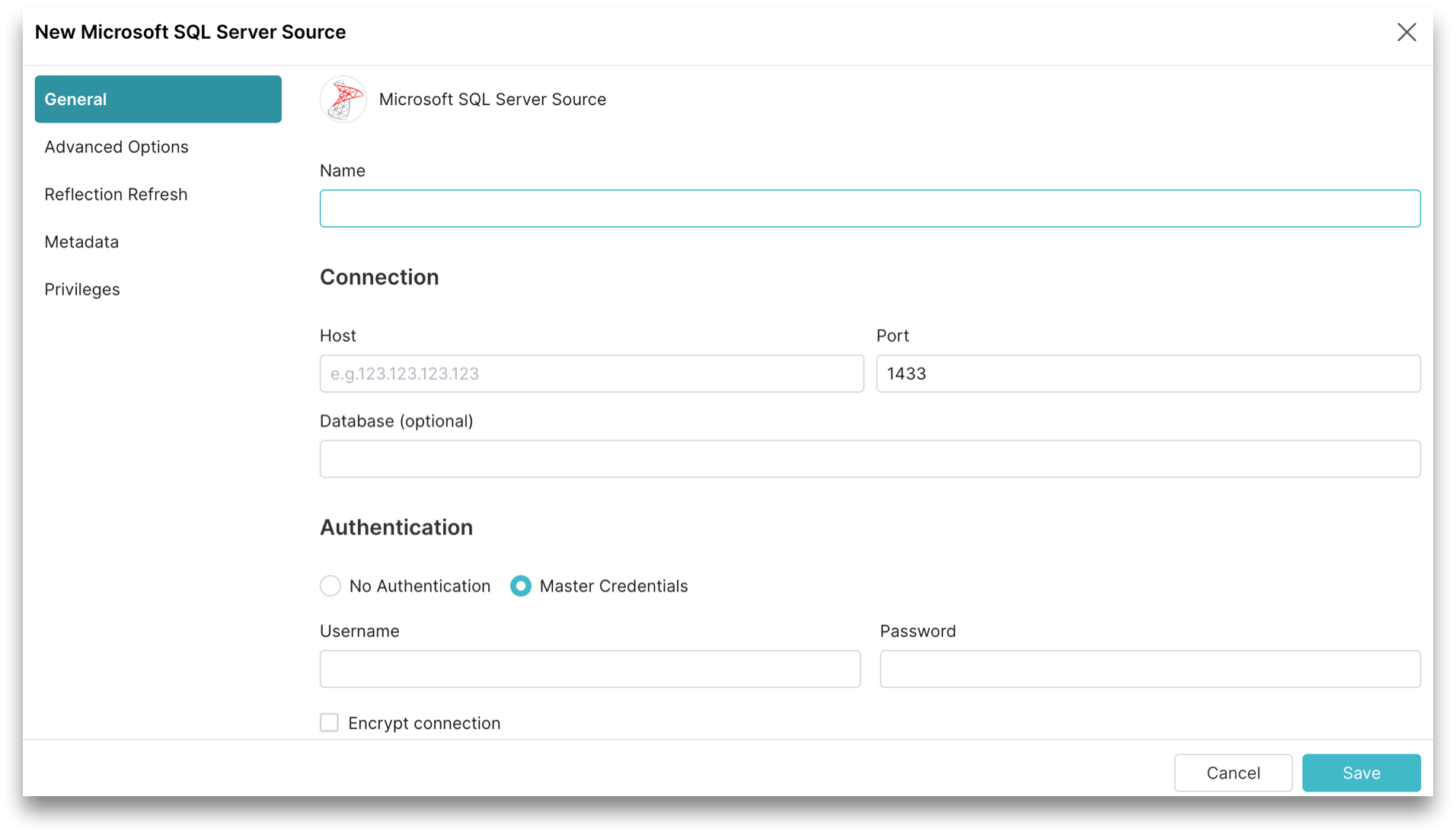
Perform these steps in the General tab:
- In the General tab, for Name, enter a name. The name cannot include the following special characters:
/,:,[, or]. - For Host, enter the Microsoft SQL Server host name.
- For Port, enter the Microsoft SQL Server port number. The default port is 1433.
- (Optional) For Database, enter the Microsoft SQL Server database name.
- (Optional) For Encrypt connection, enable encrypted connections to Microsoft SQL Server using SSL.
- For Authentication, Master Authentication is the default and the only option. Provide the username and password of a master database user with permissions to read required objects:
- For Username, enter your Microsoft SQL Server database username.
- For Password, enter your Microsoft SQL Server database password.
Advanced Options
Click Advanced Options in the sidebar.
All advanced options are optional.
| Advanced Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Show only the initial database used for connecting | If selected, hides the other databases that the credential has access to. |
| Record fetch size | Number of records to fetch at once. Set to 0 (zero) to have Sonar automatically decide. The default record fetch size is 200. |
| Maximum idle connections | The total number of connections allowed to be idle at a given time. The default maximum idle connections is 8. |
| Connection idle time (s) | The amount of time (in seconds) allowed for a connection to remain idle before the connection is terminated. The default connection idle time is 60 seconds. |
| Query timeout (s) | The amount of time (in seconds) allowed to wait for the results of a query. If this time expires, the connection being used is returned to an idle state. |
| Enable user impersonation | Select the checkbox to allow users to run queries using their credentials rather than those of the user specified in the Authentication configuration. Some setup is required in Microsoft SQL Server to allow one user to impersonate another user. Read User Impersonation for more information. |
| Encryption | Verify Server Certificate is enabled. Add an SSL/TLS server certificate distinguished name in the text box. |
| Connection Properties | Custom key value pairs for the connection relevant to the source. To add a connection property, click Add property and add the property name and value. |
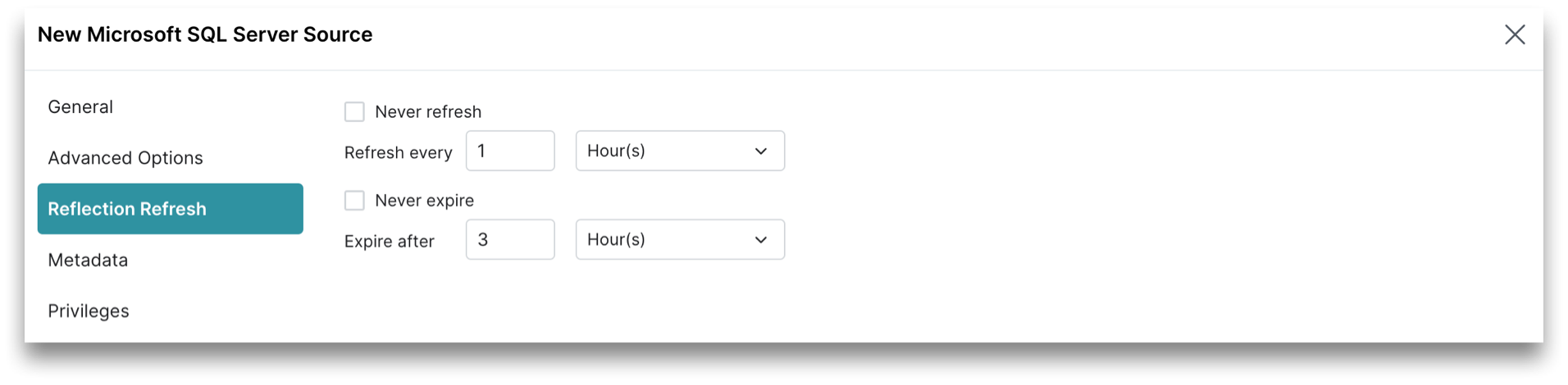
Reflection Refresh
The Reflection Refresh tab in the sidebar allows you to set time intervals for Reflections to refresh or expire.
Metadata
You can configure settings to refresh metadata and handle datasets. Click Metadata in the sidebar.
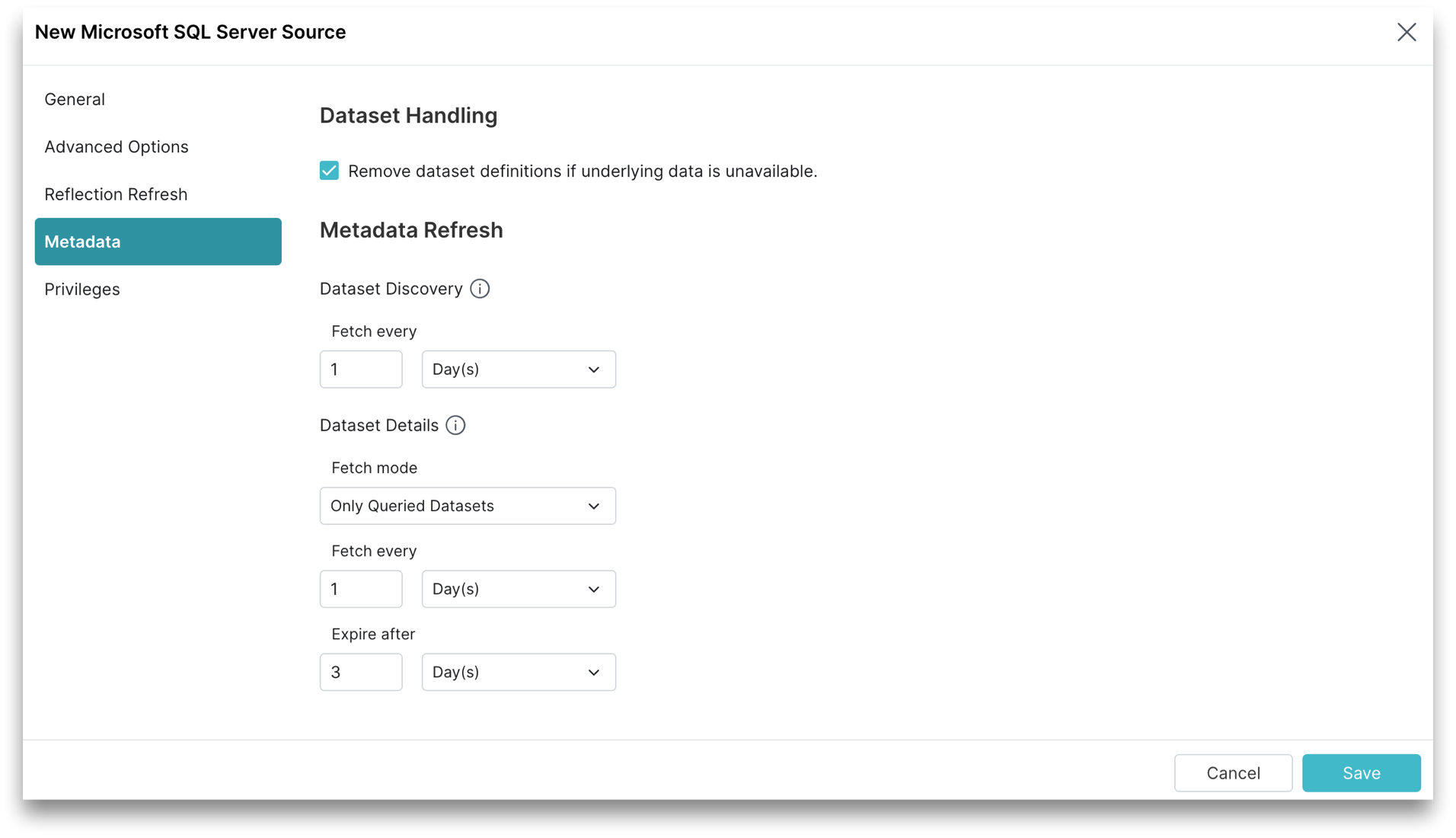
You can configure Dataset Handling and Metadata Refresh parameters.
Dataset Handling
These are the Dataset Handling parameters.
All Dataset Handling parameters are optional.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remove dataset definitions if underlying data is unavailable | By default, Sonar removes dataset definitions if underlying data is unavailable. Useful when files are temporarily deleted and added back in the same location with new sets of files. |
Metadata Refresh
These are the Metadata Refresh parameters:
-
Dataset Discovery: The refresh interval for fetching top-level source object names such as databases and tables. Set the time interval using this parameter.
Parameter Description (Optional) Fetch every You can choose to set the frequency to fetch object names in minutes, hours, days, or weeks. The default frequency to fetch object names is 1 hour. -
Dataset Details: The metadata that Sonar needs for query planning such as information required for fields, types, shards, statistics, and locality. These are the parameters to fetch the dataset information.
noteAll Dataset Details parameters are optional.
Parameter Description Fetch mode You can choose to fetch only from queried datasets that are set by default. Sonar updates details for previously queried objects in a source. Fetching from all datasets is deprecated. Fetch every You can choose to set the frequency to fetch dataset details in minutes, hours, days, or weeks. The default frequency to fetch dataset details is 1 hour. Expire after You can choose to set the expiry time of dataset details in minutes, hours, days, or weeks. The default expiry time of dataset details is 3 hours.
Privileges
Grant privileges on the source to specific users and roles. Read Privileges for more information about privileges.
To add source-specific privileges:
- Enter a user or role name under Add User/Role, click to select the user or role, and click the Add to Privileges button. The added user or role is displayed in the Users/Roles table.
- For each user or role listed in the Users/Roles table, select the checkboxes for each privilege you want to grant on the source.
- Click Save.
Editing a Microsoft SQL Server Source
To edit a Microsoft SQL Server source:
-
On the Datasets page, click Databases. A list of databases is displayed.
-
Hover over the database and click Settings
 that appears next to the database.
that appears next to the database. -
In the Source Settings dialog, you cannot edit the name. Editing other parameters is optional.
-
Click Save.
Removing a Microsoft SQL Server Source
To remove a Microsoft SQL Server source, perform these steps:
-
On the Datasets page, click Databases. A list of sources is displayed.
-
Hover over the source and click the More (...) icon that appears next to the source.
-
From the list of actions, click Remove Source. Confirm that you want to remove the source.
cautionRemoving a source causes all downstream views dependent on objects in this source to break.
noteSources containing a large number of files or tables may take longer to be removed. During this time, the source name is grayed out and shows a spinner icon, indicating the source is being removed. Once complete, the source disappears.
Predicate Pushdowns
Dremio offloads these operations to Microsoft SQL Server.
*, +, -, /, %
<, <=, <>, =, >, >=, !=
AND, NOT, OR, ||
ABS
ACOS
ADD_MONTHS
ASIN
ATAN
ATAN2
AVG
CAST
CEIL
CEILING
CHAR_LENGTH
CHARACTER_LENGTH
CONCAT
COS
COT
DATE_ADD
DATE_SUB
DATE_TRUNC_DAY
DATE_TRUNC_HOUR
DATE_TRUNC_MINUTE
DATE_TRUNC_MONTH
DATE_TRUNC_YEAR
DEGREES
E
EXP
EXTRACT_DAY
EXTRACT_DOW
EXTRACT_DOY
EXTRACT_HOUR
EXTRACT_MINUTE
EXTRACT_MONTH
EXTRACT_QUARTER
EXTRACT_SECOND
EXTRACT_WEEK
EXTRACT_YEAR
FLOOR
IS DISTINCT FROM
IS NOT DISTINCT FROM
IS NOT NULL
IS NULL
LAST_DAY
LCASE
LEFT
LENGTH
LIKE
LN
LOCATE
LOG
LOG10
LOWER
LPAD
LTRIM
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
MOD
MONTH
PERCENT_CONT
PERCENT_DISC
PI
POSITION
POW
POWER
RADIANS
RAND
REPLACE
REVERSE
RIGHT
ROUND
RPAD
RTRIM
SIGN
SIN
SQRT
SUBSTR
SUBSTRING
SUM
TAN
TIMESTAMPADD_DAY
TIMESTAMPADD_HOUR
TIMESTAMPADD_MINUTE
TIMESTAMPADD_MONTH
TIMESTAMPADD_QUARTER
TIMESTAMPADD_SECOND
TIMESTAMPADD_YEAR
TIMESTAMPDIFF_DAY
TIMESTAMPDIFF_HOUR
TIMESTAMPDIFF_MINUTE
TIMESTAMPDIFF_MONTH
TIMESTAMPDIFF_QUARTER
TIMESTAMPDIFF_SECOND
TIMESTAMPDIFF_WEEK
TIMESTAMPDIFF_YEAR
TO_DATE
TRIM
TRUNC
TRUNCATE
UCASE
UPPER
YEAR
Since Microsoft SQL Server has no Boolean type, project operations that contain SQL expressions which evaluate to true or false (e.g. SELECT username, friends > 0), and filter operations that include Boolean literals in a filter (e.g. WHERE currentAccount = true) cannot be executed as pushdowns.