Connect to a Dremio Enterprise Cluster
Connect your project to one or more Dremio Enterprise clusters to create a federated data architecture that combines the best of both environments.
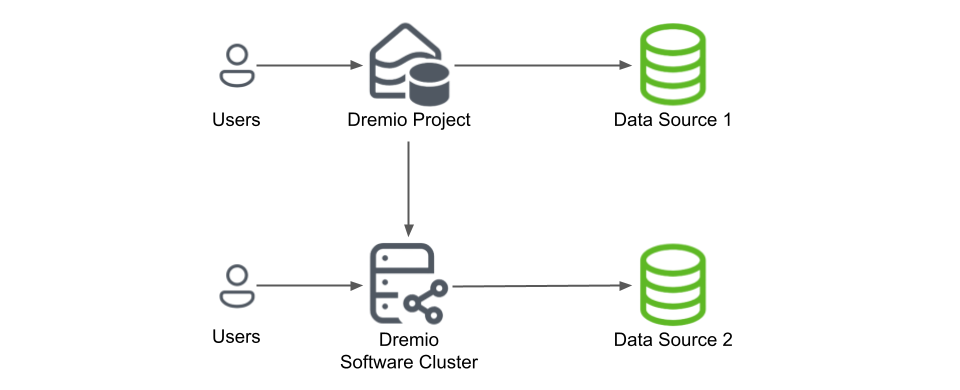
This configuration enables:
- Reduced query latency – Queries or portions of queries that utilize tables on the Enterprise cluster are pushed down to maximize performance and reduce latency compared to transporting large raw tables.
- Cross-cluster data federation – Join data across multiple Dremio Enterprise clusters and expose unified views through Dremio.
- Enhanced security and data isolation – Expose only a single Dremio port to the cloud instead of opening multiple source connections from your data center. Administrators of the Enterprise cluster control what data is visible to the managing Dremio environment, allowing isolation of highly sensitive data on the Enterprise cluster while exposing only aggregations or derived datasets to the managing project.
- Simplified data access – Access all data sources connected to Enterprise clusters as schemas within Dremio without managing individual source connections.
- Centralized semantic layer – Build views and virtual datasets on top of federated clusters for consistent business logic across your organization.
When you connect a Dremio Enterprise cluster as a data source, all sources on the Enterprise cluster can be available from your project. You can create Reflections, build views, and query across the federated environment just as you would with any connected source.
Example Configuration
When you add a Dremio Enterprise cluster as a source to your Dremio project:
- The Enterprise cluster appears under Sources > Databases in your project.
- Data sources connected to the Enterprise cluster appear as folders/schemas.
- You can promote tables from both directly connected sources and federated sources.
- Create views and Reflections on any promoted tables, regardless of source type.
- Query and join data across all sources—direct and federated.
Deployment Considerations
If your Dremio project and the source Dremio Enterprise cluster are in different cloud regions or cloud vendors, your deployment design may be influenced by network latency and egress costs.
Network Latency
Cross-region or cross-cloud queries can experience increased latency. To minimize impact:
- Use Reflections – Create Reflections in your Dremio project of frequently queried data from the Enterprise cluster. Queries use the Reflections instead of fetching data across regions.
- Push down filters and aggregations – Write queries that leverage Dremio's query pushdown to perform filtering and aggregation on the Enterprise cluster before returning results.
- Colocate when possible – If latency is critical, deploy the Enterprise cluster in the same region as your Dremio organization.
Cloud Egress Costs
Data transfer between cloud regions or cloud vendors can incur significant egress charges. To control costs:
- Create Reflections for frequently used data – Reflection data is stored in your Dremio region, eliminating repeated egress charges for frequently accessed datasets.
- Use aggregated views – Expose only aggregated or summarized data from the Enterprise cluster rather than raw tables, reducing data transfer volume.
- Limit full table scans – Ensure queries include appropriate filters to minimize the amount of data transferred across regions.
- Monitor query patterns – Use Dremio's query history to identify expensive cross-region queries and optimize them with Reflections.
Security
Configure full TLS wire encryption on Enterprise clusters to protect data in transit across regions and cloud boundaries.
User Impersonation
When you connect your project to a Dremio Enterprise cluster, you provide the username and password of an account on the cluster. By default, queries that run from the project against the Dremio Enterprise cluster run under the username of that account.
Alternatively, you can utilize user impersonation, which allows users running queries from your project to run them under their own usernames on the Dremio Enterprise cluster. Users in your project must have accounts on the Dremio Enterprise cluster, and the usernames must match. User impersonation (also known as Inbound Impersonation) must be set up on the Dremio Enterprise cluster. The policy for user impersonation would look like this:
Example policyALTER SYSTEM SET "exec.impersonation.inbound_policies"='[
{
"proxy_principals":{
"users":[
"User_1"
]
},
"target_principals":{
"users":[
"User_1"
]
}
}
]'
Prerequisites
You must have a username and password for the account on the Dremio Enterprise cluster to use for connections from your project.
Configure a Dremio Enterprise Cluster as a Source
- In the bottom-left corner of the Datasets page, click Add Data.
- Under Databases in the Add Data Source dialog, select Dremio.
General Options
- In the Name field, specify the name by which you want the data-source cluster to appear in the Databases section. The name cannot include the following special characters:
/,:,[, or]. - Under Connection, specify how you want to connect to the data-source cluster:
- Direct: Connect directly to a coordinator node of the cluster.
- ZooKeeper: Connect to an external ZooKeeper instance that is coordinating the nodes of the cluster.
- In the Host and Port fields, specify the hostname or IP address and the port number of the coordinator node or ZooKeeper instance.
- If the data-source cluster is configured to use TLS for connections to it, select the Use SSL option.
- Under Authentication, specify the username and password for the project to use when connecting to the data-source cluster.
Advanced Options
On the Advanced Options page, you can set values for these optional parameters:
- Maximum Idle Connections – The total number of connections allowed to be idle at a given time. The default is 8.
- Connection Idle Time – The amount of time (in seconds) allowed for a connection to remain idle before the connection is terminated. The default is 60 seconds.
- Query Timeout – The amount of time (in seconds) allowed to wait for the results of a query. If this time expires, the connection being used is returned to an idle state.
- User Impersonation – Allows users to run queries on the data-source cluster under their own user IDs, not the user ID for the account used to authenticate with the data-source cluster. Inbound impersonation must be configured on the data-source cluster.
Reflection Refresh Options
On the Reflection Refresh page, set the policy that controls how often Reflections are scheduled to be refreshed automatically, as well as the time limit after which Reflections expire and are removed.
- Never refresh – Select to prevent automatic Reflection refresh. The default is to automatically refresh.
- Refresh every – How often to refresh Reflections, specified in hours, days, or weeks. This option is ignored if Never refresh is selected.
- Never expire – Select to prevent Reflections from expiring. The default is to automatically expire after the time limit below.
- Expire after – The time limit after which Reflections expire and are removed from Dremio, specified in hours, days, or weeks. This option is ignored if Never expire is selected.
Metadata Options
On the Metadata page, you can configure settings to refresh metadata and handle datasets.
Dataset Handling
- Remove dataset definitions if underlying data is unavailable – By default, Dremio removes dataset definitions if underlying data is unavailable. This is useful when files are temporarily deleted and added back in the same location with new sets of files.
Metadata Refresh
These are the optional Metadata Refresh parameters:
- Dataset Discovery: The refresh interval for fetching top-level source object names such as databases and tables. Set the time interval using this parameter.
- Fetch every (Optional) – You can choose to set the frequency to fetch object names in minutes, hours, days, or weeks. The default is 1 hour.
- Dataset Details: The metadata that Dremio needs for query planning, such as information required for fields, types, shards, statistics, and locality. These are the parameters to fetch the dataset information:
- Fetch mode – You can choose to fetch only from queried datasets, which is set by default. Dremio updates details for previously queried objects in a source. Fetching from all datasets is deprecated.
- Fetch every – You can choose to set the frequency to fetch dataset details in minutes, hours, days, or weeks. The default is 1 hour.
- Expire after – You can choose to set the expiry time of dataset details in minutes, hours, days, or weeks. The default is 3 hours.
Privileges
On the Privileges page, you can grant privileges to specific users or roles. See Access Control for additional information about user privileges.
- (Optional) For Privileges, enter the username or role name that you want to grant access to and click the Add to Privileges button. The added user or role is displayed in the Users table.
- (Optional) For the users or roles in the Users table, toggle the green checkmark for each privilege you want to grant on the Dremio source that is being created.
- Click Save after setting the configuration.
Update a Dremio Source
To edit a Dremio source:
- On the Datasets page, under Databases, find the name of the source you want to edit.
- Right-click the source name and select Settings from the list of actions.
- In the Source Settings dialog, edit the settings you wish to update. Dremio does not support updating the source name. For information about the settings options, see Configure a Dremio Enterprise Cluster as a Source.
- Click Save.
Remove a Dremio Source
To remove a Dremio source, perform these steps:
- On the Datasets page, under Databases, find the name of the source you want to remove.
- In the list of data sources, hover over the name of the source you want to remove and right-click.
- From the list of actions, click Delete.
- In the Delete Source dialog, click Delete to confirm that you want to remove the source.
Predicate Pushdowns
Projects offload these operations to data-source clusters. Data-source clusters either process these operations or offload them to their connected data sources.
&&, ||, !, AND, OR
+, -, /, *, %
<=, <, >, >=, =, <>, !=
ABS
ADD_MONTHS
AVG
BETWEEN
CASE
CAST
CEIL
CEILING
CHARACTER_LENGTH
CHAR_LENGTH
COALESCE
CONCAT
CONTAINS
COUNT
COUNT_DISTINCT
COUNT_DISTINCT_MULTI
COUNT_FUNCTIONS
COUNT_MULTI
COUNT_STAR
CURRENT_DATE
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
DATE_ADD
DATE_DIFF
DATE_SUB
DATE_TRUNC
DATE_TRUNC_DAY
DATE_TRUNC_HOUR
DATE_TRUNC_MINUTE
DATE_TRUNC_MONTH
DATE_TRUNC_QUARTER
DATE_TRUNC_WEEK
DATE_TRUNC_YEAR
DAYOFMONTH
DAYOFWEEK
DAYOFYEAR
EXTRACT
FLATTEN
FLOOR
ILIKE
IN
IS DISTINCT FROM
IS NOT DISTINCT FROM
IS NOT NULL
IS NULL
LAST_DAY
LCASE
LEFT
LENGTH
LIKE
LOCATE
LOWER
LPAD
LTRIM
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
MOD
NEXT_DAY
NOT
NVL
PERCENTILE_CONT
PERCENTILE_DISC
PERCENT_RANK
POSITION
REGEXP_LIKE
REPLACE
REVERSE
RIGHT
ROUND
RPAD
RTRIM
SIGN
SQRT
STDDEV
STDDEV_POP
STDDEV_SAMP
SUBSTR
SUBSTRING
SUM
TO_CHAR
TO_DATE
TRIM
TRUNC
TRUNCATE
UCASE
UPPER
VAR_POP
VAR_SAMP
Limitations
You cannot query columns that use complex data types, such as LIST, STRUCT, and MAP. Columns of complex data types do not appear in result sets.