Amazon Redshift
Configuring Amazon Redshift as a Source
- On the Datasets page, to the right of Sources in the left panel, click
 .
. - In the Add Data Source dialog, under Databases, select Amazon Redshift.
General
Under Name, enter the name to identify the data source in Dremio. The name cannot include the following special characters: /, :, [, or ].
Connection
- JDBC Connection String -- Connection string. The connection URL can be found in AWS console.
Authentication
Select an authentication option:
- No Authentication
- Master Credentials (default):
- Username: Redshift username
- Password: Select the password store from the dropdown menu:
- Dremio: Provide the password in plain text. Dremio stores the password.
- Azure Key Vault: Provide the URI for your stored password using the format
https://<vault_name>.vault.azure.net/secrets/<secret_name> - AWS Secrets Manager: Provide the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the AWS Secrets Manager secret that holds the password, which is available in the AWS web console or using command line tools.
- HashiCorp Vault: Select your HashiCorp secrets engine from the dropdown and enter the password reference in the correct format.
- Secret Resource URL: Provide the Username and Secret Resource URL to use for authentication.
- EKS Pod Identity: Dremio uses the IAM policy associated with the coordinator's Kubernetes service account.
- AWS Profile: Dremio sources profile credentials from the specified AWS profile. For information on how to set up a configuration or credentials file for AWS, see AWS Custom Authentication.
- AWS Profile (Optional): The AWS profile name. If this is left blank, then the default profile will be used. For more information about using profiles in a credentials or configuration file, see AWS's documentation on Configuration and credential file settings.
- DbUser (Optional): The name of the Redshift DbUser to use for authentication. If this is left blank, the default user name for your AWS IAM role will be used (generally this is the same as your AWS username).
Advanced Options
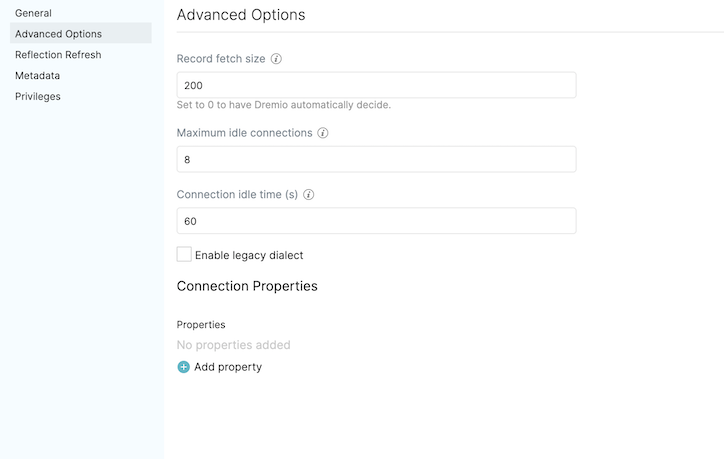 !
!- Record fetch size: Number of records to fetch at once. Set to 0 (zero) to have Dremio automatically decide. Default: 10
- Maximum idle connections: The total number of connections allowed to be idle at a given time. By default, this is set to 8.
- Connection idle time (s): The amount of time (in seconds) allowed for a connection to remain idle before the connection is terminated. By default, this is set to 60.
- Query timeout: The amount of time (in seconds) allowed to wait for the results of a query. If this time expires, the connection being used is returned to an idle state.
- Enable legacy dialect
Reflection Refresh
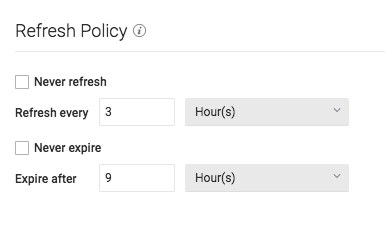
- Never refresh -- Specifies how often to refresh based on hours, days, weeks, or never.
- Never expire -- Specifies how often to expire based on hours, days, weeks, or never.
Metadata
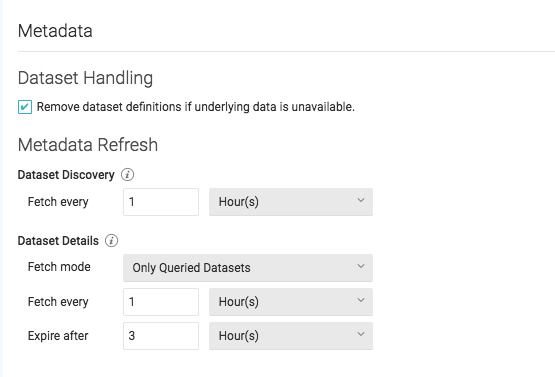
Dataset Handling
- Remove dataset definitions if underlying data is unavailable (Default).
If this box is not checked and the underlying files under a folder are removed or the folder/source is not accessible, Dremio does not remove the dataset definitions. This option is useful in cases when files are temporarily deleted and put back in place with new sets of files.
Metadata Refresh
- Dataset Discovery -- Refresh interval for top-level source object names such as names of DBs and tables.
- Fetch every -- Specify fetch time based on minutes, hours, days, or weeks. Default: 1 hour
- Dataset Details -- The metadata that Dremio needs for query planning such as information needed for
fields, types, shards, statistics, and locality.
- Fetch mode -- Specify either Only Queried Datasets, All Datasets, or As Needed. Default: Only Queried Datasets
- Only Queried Datasets -- Dremio updates details for previously queried objects in a source.
This mode increases query performance because less work is needed at query time for these datasets. - All Datasets -- Dremio updates details for all datasets in a source. This mode increases query performance because less work is needed at query time.
- As Needed -- Dremio updates details for a dataset at query time. This mode minimized metadata queries on a source when not used, but might lead to longer planning times.
- Only Queried Datasets -- Dremio updates details for previously queried objects in a source.
- Fetch every -- Specify fetch time based on minutes, hours, days, or weeks. Default: 1 hour
- Expire after -- Specify expiration time based on minutes, hours, days, or weeks. Default: 3 hours
- Fetch mode -- Specify either Only Queried Datasets, All Datasets, or As Needed. Default: Only Queried Datasets
Privileges
On the Privileges tab, you can grant privileges to specific users or roles. See Access Controls for additional information about privileges. All privileges are optional.
- For Privileges, enter the user name or role name that you want to grant access to and click the Add to Privileges button. The added user or role is displayed in the USERS/ROLES table.
- For the users or roles in the USERS/ROLES table, toggle the checkmark for each privilege you want to grant on the Dremio source that is being created.
- Click Save after setting the configuration.
Updating an Amazon Redshift Source
To update an Amazon Redshift source:
- On the Datasets page, under Databases in the panel on the left, find the name of the source you want to update.
- Right-click the source name and select Settings from the list of actions. Alternatively, click the source name and then the
 at the top right corner of the page.
at the top right corner of the page. - In the Source Settings dialog, edit the settings you wish to update. Dremio does not support updating the source name. For information about the settings options, see Configuring Amazon Redshift as a Source.
- Click Save.
Deleting an Amazon Redshift Source
If the source is in a bad state (for example, Dremio cannot authenticate to the source or the source is otherwise unavailable), only users who belong to the ADMIN role can delete the source.
To delete an Amazon Redshift source, perform these steps:
- On the Datasets page, click Sources > Databases in the panel on the left.
- In the list of data sources, hover over the name of the source you want to remove and right-click.
- From the list of actions, click Delete.
- In the Delete Source dialog, click Delete to confirm that you want to remove the source.
Deleting a source causes all downstream views that depend on objects in the source to break.
Predicate Pushdowns
Dremio delegates the execution of these expressions and functions to the database being queried, often dramatically improving query performance. It can also offload entire SQL queries that include one or more of these expressions and functions.
*, +, -, /
<, <=, <>, =, >, >=, !=
AND, NOT, OR, ||
ABS
ACOS
ADD_MONTHS
ASIN
ATAN
ATAN2
AVG
CAST
CBRT
CEIL
CEILING
CHAR_LENGTH
CHARACTER_LENGTH
CONCAT
COS
COT
DATE_ADD
DATE_SUB
DATE_TRUNC_CENTURY
DATE_TRUNC_DAY
DATE_TRUNC_DECADE
DATE_TRUNC_HOUR
DATE_TRUNC_MINUTE
DATE_TRUNC_MONTH
DATE_TRUNC_QUARTER
DATE_TRUNC_SECOND
DATE_TRUNC_WEEK
DATE_TRUNC_YEAR
DEGREES
E
EXP
EXTRACT_CENTURY
EXTRACT_DAY
EXTRACT_DECADE
EXTRACT_DOW
EXTRACT_DOY
EXTRACT_EPOCH
EXTRACT_HOUR
EXTRACT_MILLENNIUM
EXTRACT_MINUTE
EXTRACT_MONTH
EXTRACT_QUARTER
EXTRACT_SECOND
EXTRACT_WEEK
EXTRACT_YEAR
FLOOR
IS DISTINCT FROM
IS NOT DISTINCT FROM
IS NOT NULL
IS NULL
LAST_DAY
LCASE
LEFT
LENGTH
LIKE
LN
LOCATE
LOG
LOG10
LOWER
LPAD
LTRIM
MAX
MEDIAN
MIN
MOD
PERCENT_CONT
PERCENT_DISC
PI
POSITION
POW
POWER
RADIANS
REPLACE
REVERSE
RIGHT
ROUND
RPAD
RTRIM
SIGN
SIN
SQRT
STDDEV
STDDEV_POP
STDDEV_SAMP
SUBSTR
SUBSTRING
SUM
TAN
TIMESTAMPADD_DAY
TIMESTAMPADD_HOUR
TIMESTAMPADD_MINUTE
TIMESTAMPADD_MONTH
TIMESTAMPADD_QUARTER
TIMESTAMPADD_SECOND
TIMESTAMPADD_WEEK
TIMESTAMPADD_YEAR
TIMESTAMPDIFF_DAY
TIMESTAMPDIFF_HOUR
TIMESTAMPDIFF_MINUTE
TIMESTAMPDIFF_MONTH
TIMESTAMPDIFF_QUARTER
TIMESTAMPDIFF_SECOND
TIMESTAMPDIFF_WEEK
TIMESTAMPDIFF_YEAR
TO_CHAR
TO_DATE
TRIM
TRUNC
TRUNCATE
UCASE
UPPER
VAR_POP
VAR_SAMP
Running Queries Directly on Redshift Through Dremio
Dremio users can run pass queries through Dremio to run on Redshift. Doing so can sometimes decrease query execution times. For more information, see Querying Relational-Database Sources Directly.
For More Information
- See Redshift Data Types for information about mapping to Dremio data types.