Manual Reflections
With Autonomous Reflections reducing the need for manual work, you no longer need to create or manage Reflections. However, when Autonomous Reflections are not enabled or for situations that require manual control, this page provides guidance on getting Reflection recommendations and how to manage raw Reflections, aggregation Reflections, and external Reflections in Dremio.
For non-duplicating joins, Dremio can accelerate queries that reference only some of the joins in a Reflection, eliminating the need to create separate Reflections for every table combination.
Reflection Recommendations
When Autonomous Reflections are not enabled, Dremio automatically provides recommendations to add and remove Reflections based on query patterns to optimize performance for queries on Iceberg tables, UniForm table, Parquet datasets, and any views built on these datasets.
Recommendations to add Reflections are sorted by overall effectiveness, with the most effective recommendations shown on top. Effectiveness relates to metrics such as the estimated number of accelerated jobs, potential increase in query execution speedup, and potential time saved during querying. These are rough estimates based on past data that can give you insight into the potential benefits of each recommendation. Reflections created using these recommendations refresh automatically when source data changes on:
- Iceberg tables – When the table is modified through Dremio or other engines. Dremio polls tables every 10 seconds.
- Parquet datasets – When metadata is updated in Dremio.
To view and apply the Reflection recommendations:
- In the Dremio console, hover over
 in the side navigation bar and select Project Settings.
in the side navigation bar and select Project Settings. - Select Reflections from the project settings sidebar.
- Click Reflections Recommendations to access the list of suggested Reflections.
- To apply a recommendation, click
 at the end of the corresponding row.
at the end of the corresponding row.
Reflections created using usage-based recommendations are only used when fully synchronized with their source data to ensure up-to-date query results.
To generate recommendations for default raw and aggregation Reflections, you can obtain the job IDs by looking them up on the Jobs page. Then, use either the SYS.RECOMMEND_REFLECTIONS table function or the Recommendations API to submit job IDs to accelerate specific SQL queries.
Raw Reflections
Retain the same number of records as its anchor while allowing a subset of columns. It enhances query performance by materializing complex views, transforming data from non-performant sources into the Iceberg table format optimized for large-scale analytics, and utilizing partitioning and sorting for faster access. By precomputing and storing data in an optimized format, raw Reflections significantly reduce query latency and improve overall efficiency.
You can use the Reflections editor to create two types of raw Reflection:
-
A default raw Reflection that includes all of the columns of the anchor, but does not sort or horizontally partition on any columns
-
A raw Reflection that includes all or a subset of the columns of the anchor, and that does one or both of the following things:
- Sorts on one or more columns
- Horizontally partitions the data according to the values in one or more columns
For creating Reflections on views and tables with row-access and column-masking policies, see Use Reflections on Datasets with Policies.
Prerequisites
- If you want to accelerate queries on unoptimized data or data in slow storage, create a view that is itself created from a table in a non-columnar format or on slow-scan storage. You can then create your raw Reflection from that view.
- If you want to accelerate "needle-in-a-haystack" queries, create a view that includes a predicate to include only the rows that you want to scan. You can then create your raw Reflection from that view.
- If you want to accelerate queries that perform expensive transformations, create a view that performs those transformations. You can then create your raw Reflection from that view.
- If you want to accelerate queries that perform joins, create a view that performs the joins. You can then create your raw Reflection from that view.
Create Default Raw Reflections
In the Basic view of the Reflections editor, you can create a raw Reflection that includes all of the fields that are in a table or view. Creating a basic raw Reflection ensures that Dremio never runs user queries against the underlying table or view when the raw Reflection is enabled.
To create a raw Reflection in the Basic view of the Reflections editor:
-
In the Dremio console, click
 in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page.
in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page. -
In the catalog or folder in which the anchor is located, hover over the anchor name and click
 .
. -
Select Reflections in the table or view settings sidebar.
-
Click the toggle switch on the left side of the Raw Reflections bar.
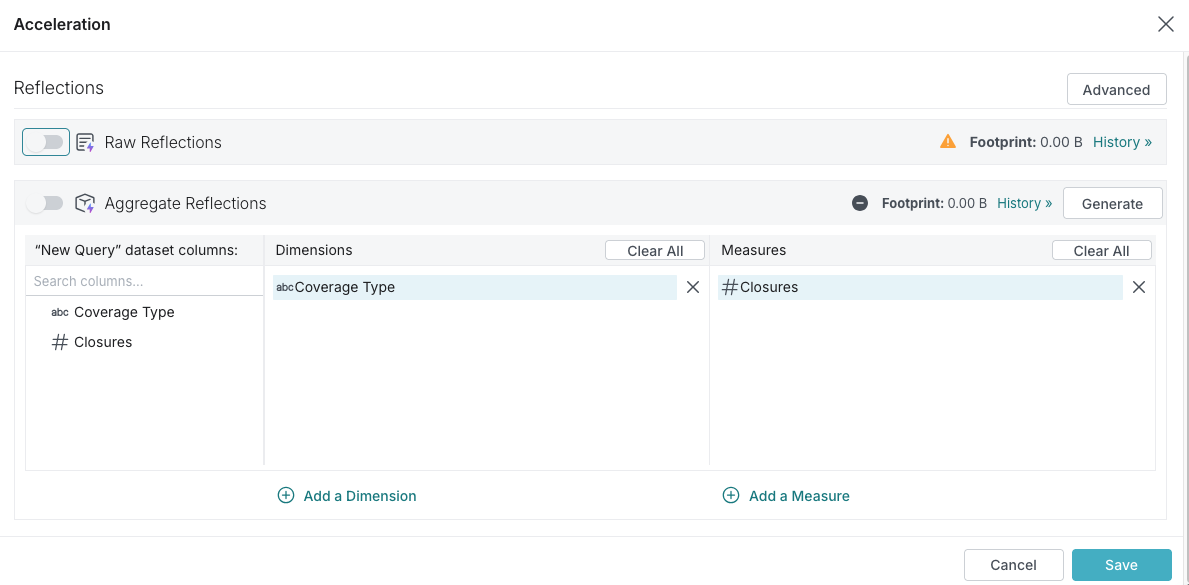
-
Click Save.
Restrictions of the Basic View
- You cannot select fields to sort or create horizontal partitions on.
- The name of the Reflection that you create is restricted to "Raw Reflection".
- You can create only one raw Reflection. If you want to create multiple raw Reflections at a time, use the Advanced view.
Create Customized Raw Reflections
In the Advanced view of the Reflections editor, you can create one or more raw Reflections that include all or a selection of the fields that are in the anchor or supported anchor. You can also choose sort fields and fields for partitioning horizontally.
Dremio recommends that you follow the best practices listed in Operational Excellence when you create customized raw Reflections.
If you make any of the following changes to a raw Reflection when you are using the Advanced view, you cannot switch to the Basic view:
- Deselect one or more fields in the Display column. By default, all of the fields are selected.
- Select one or more fields in the Sort, Partition, or Distribute column.
To create a raw Reflection in the Advanced view of the Reflections editor:
-
In the Dremio console, click
 in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page.
in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page. -
In the catalog or folder in which the anchor is located, hover over the anchor name and click
 .
. -
If the Advanced view is not already displayed, click the Advanced View button in the top-right corner of the editor.
-
Click the toggle switch in the table labeled Raw Reflection to enable the raw Reflection.
Queries do not start using the Reflection, however, until after you have finished editing the Reflection and click Save in a later step.
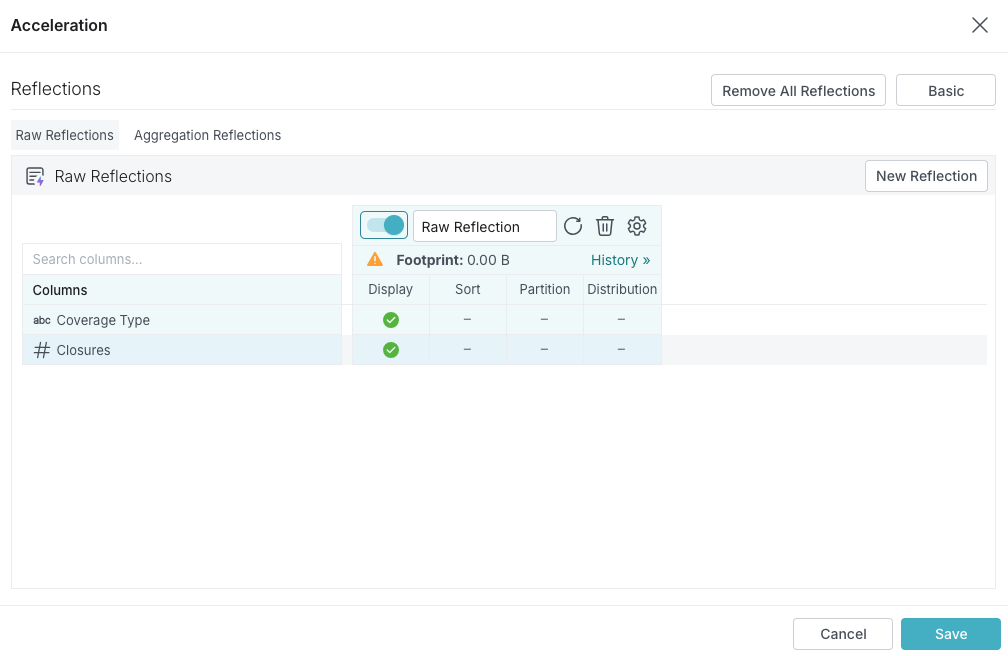
-
(Optional) Click in the label to rename the Reflection.
The purpose of the name is to help you understand, when you read job reports, which Reflections the query optimizer considered and chose when planning queries.
-
In the columns of the table, follow these steps, which you don't have to do in any particular order:
noteIgnore the Distribution column. Selecting fields in it has no effect on the Reflection.
-
Click in the Display column to include fields in or exclude them from your Reflection.
-
Click in the Sort column to select fields on which to sort the data in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting a field on which to sort, see Sort Reflections on High-Cardinality Fields.
-
Click in the Partition column to select fields on which to horizontally partition the rows in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting fields on which to partition, and which partition transforms to apply to those fields, see Horizontally Partition Reflections that Have Many Rows.
noteIf the Reflection is based on an Iceberg table, a filesystem source, an AWS Glue source, or a Hive source, and that table is partitioned, recommended partition columns and transforms are selected for you. If you change the selection of columns, then this icon appears at the top of the table:
 . You can click it to revert to the recommended selection of partition columns.
. You can click it to revert to the recommended selection of partition columns.
-
-
(Optional) Optimize the number of files used to store the Reflection. You can optimize for fast refreshes or for fast read performance by queries. Follow these steps:
a. Click the
 in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.
in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.b. In the field Reflection execution strategy, select either of these options:
- Select Minimize Time Needed To Refresh if you need the Reflection to be created as fast as possible. This option can result in the data for the Reflection being stored in many small files. This is the default option.
- Select Minimize Number Of Files when you want to improve the read performance of queries against the Reflection. With this option, there tend to be fewer seeks performed for a given query.
-
Click Save when you are finished.
Edit Raw Reflections
You can edit an existing raw Reflection. You might want to do so if you are iteratively designing and testing a raw Reflection, if the definition of the view that the Reflection was created from was changed, or if the schema of the underlying table was changed.
If you created a raw Reflection in the Basic view of the Reflections editor, you must use the Advanced view to edit it.
Dremio runs the job or jobs to recreate the Reflection after you click Save.
To edit a raw Reflection in the Advanced view of the Reflections editor:
-
In the Dremio console, hover over
 in the side navigation bar and select Project settings.
in the side navigation bar and select Project settings. -
Select Reflections in the project settings sidebar.
-
Click the name of the Reflection. This opens the Acceleration dialog with the Reflections editor.
-
Click the Advanced View button in the top-right corner of the editor.
-
In the Raw Reflections section of the Advanced view, locate the table that shows the definition of your Reflection.
-
(Optional) Click in the label to rename the Reflection.
The purpose of the name is to help you understand, when you read job reports, which Reflections the query optimizer considered and chose when planning queries.
-
In the columns of the table, follow these steps, which you don't have to do in any particular order:
-
Click in the Display column to include fields in or exclude them from your Reflection.
-
Click in the Sort column to select fields on which to sort the data in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting a field on which to sort, see Sort Reflections on High-Cardinality Fields.
-
Click in the Partition column to select fields on which to horizontally partition the rows in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting fields on which to partition, and which partition transforms to apply to those fields, see Horizontally Partition Reflections that Have Many Rows.
If the Reflection is based on an Iceberg table, a filesystem source, an AWS Glue source, or a Hive source, and that table is partitioned, partition columns and transforms are recommended for you. Hover over
 at the top of the table to see the recommendation. Click the icon to accept the recommendation.
at the top of the table to see the recommendation. Click the icon to accept the recommendation.
noteIgnore the Distribution column. Selecting fields in it has no effect on the Reflection.
-
-
(Optional) Optimize the number of files used to store the Reflection. You can optimize for fast refreshes or for fast read performance by queries. Follow these steps:
a. Click the
 in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.
in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.b. In the field Reflection execution strategy, select either of these options:
- Select Minimize Time Needed To Refresh if you need the Reflection to be created as fast as possible. This option can result in the data for the Reflection being stored in many small files. This is the default option.
- Select Minimize Number Of Files when you want to improve read performance of queries against the Reflection. With this option, there tend to be fewer seeks performed for a given query.
-
Click Save when you are finished.
Aggregation Reflections
Accelerate BI-style queries that involve aggregations (GROUP BY queries) by precomputing results (like SUM, COUNT, AVG, GROUP BY) across selected dimensions and measures. By precomputing expensive computations, they significantly improve query performance at runtime. These Reflections are ideal for analytical workloads with frequent aggregations on large datasets.
Create Default Aggregation Reflections
You can use the Basic view of the Reflections editor to create one aggregation Reflection that includes fields, from the anchor or supported anchor, that are recommended for use as dimensions or measures. You can add or remove dimensions and measures, too.
To create an aggregation Reflection in the Basic view of the Reflections editor:
-
In the Dremio console, click
 in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page.
in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page. -
In the catalog or folder in which the anchor is located, hover over the anchor name and click
 .
. -
In the Aggregations Reflections section of the editor, click Generate to get recommended fields to use as dimensions and measures. This will override any previously selected dimensions and measures. If you wish to proceed, click Continue in the confirmation dialog that follows.
-
In the Aggregation Reflection section of the editor, modify or accept the recommended fields for dimensions and measures.
-
To make the Reflection available to the query optimizer after you create it, click the toggle switch on the left side of the Aggregation Reflections bar.
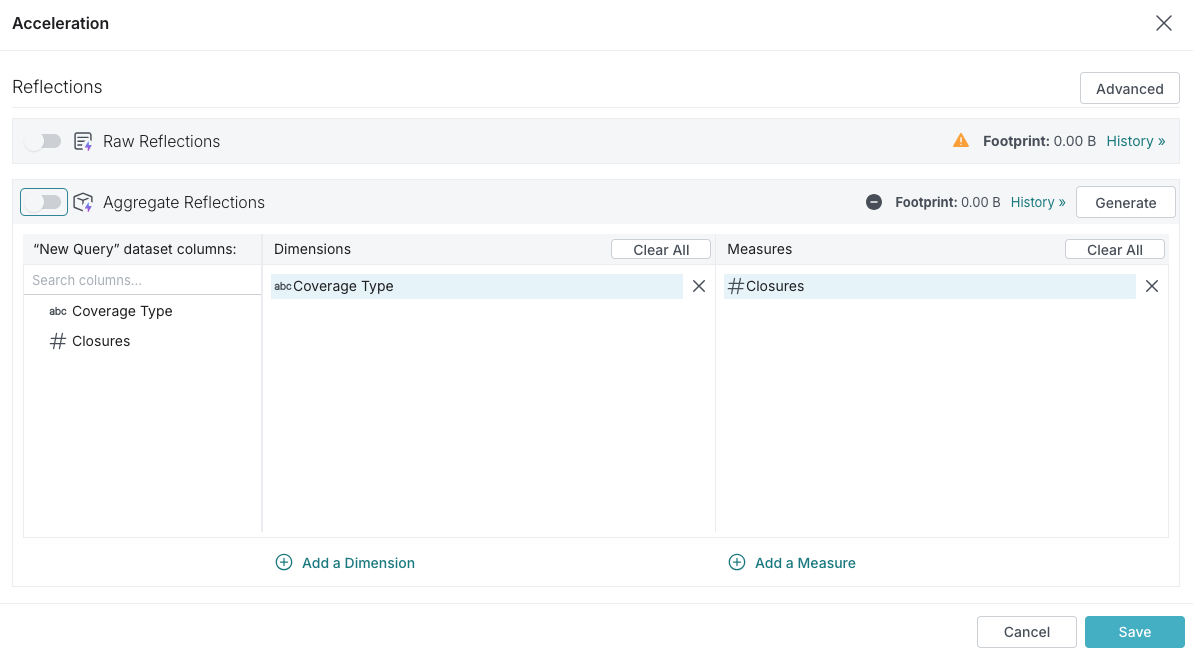
-
Click Save.
Restrictions
- You can create only one aggregation Reflection in the Basic view. If you want to create multiple aggregations Reflections at a time, use the Advanced view.
- You cannot select fields for sorting or horizontally partitioning.
- The name of the Reflection is restricted to "Aggregation Reflection".
Create Customized Aggregation Reflections
You can use the Advanced view of the Reflections editor to create one or more aggregation Reflections that select which fields in the anchor or supporting anchor to use as dimensions and measures. For each field that you use as a measure, you can use one or more of these SQL functions: APPROX_DISTINCT_COUNT, COUNT, MAX, and MIN. You can also choose sort fields and fields for partitioning horizontally.
Before you create customized aggregation Reflections, Dremio recommends that you follow the best practices listed in Operational Excellence when you create customized aggregation Reflections.
To create an aggregation Reflection in the Advanced view of the Reflections editor:
-
In the Dremio console, click
 in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page.
in the side navigation bar to go to the Datasets page. -
In the catalog or folder in which the anchor is located, hover over the anchor name and click
 .
. -
Click the Advanced View button in the top-right corner of the editor.
-
Click Aggregation Reflections.
The Aggregation Reflections section is displayed, and one table for refining the aggregation Reflection that appeared in the Basic view is ready.
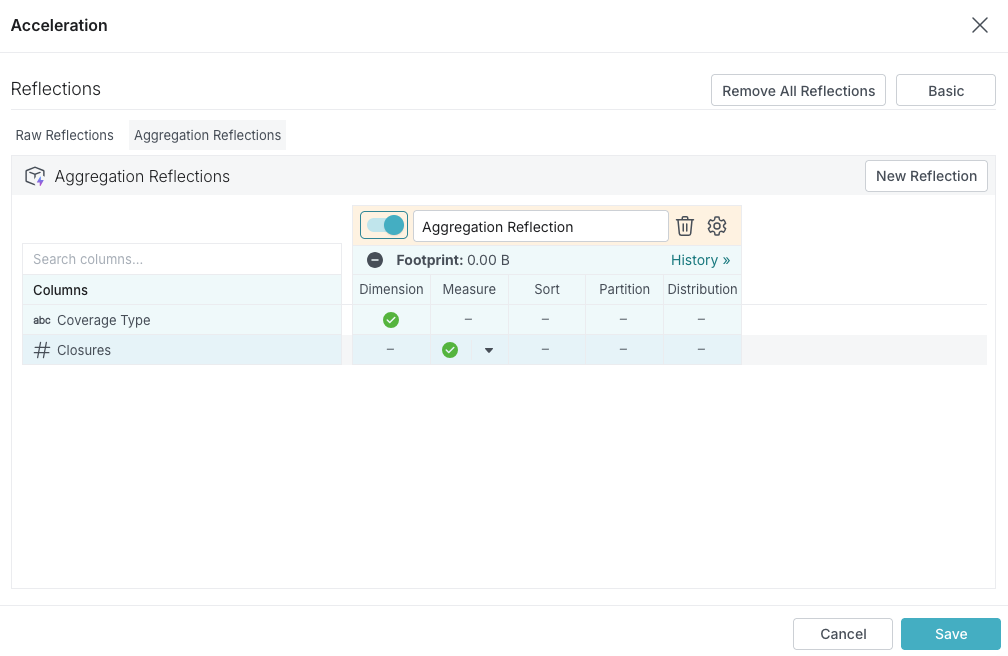
-
(Optional) Click in the name to rename the Reflection.
The purpose of the name is to help you understand, when you read job reports, which Reflections the query optimizer considered and chose when planning queries.
-
In the columns of the table, follow these steps, which you don't have to do in any particular order:
-
Click in the Dimension column to include or exclude fields to use as dimensions.
-
Click in the Measure column to include or exclude fields to use as measures. You can use one or more of these SQL functions for each measure:
APPROX_DISTINCT_COUNT,COUNT,MAX, andMIN.If you want to include a computed measure, first create a view with the computed column to use as a measure, and then create the aggregation Reflection on the view.
The full list of SQL aggregation functions that Dremio supports is not supported in the Reflections editor. If you want to create a Reflection that aggregates data by using the
AVG,CORR,HLL,SUM,VAR_POP, orVAR_SAMPSQL functions, you must create a view that uses the function, and then create a raw Reflection from that view.-
Click in the Sort column to select fields on which to sort the data in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting a field on which to sort, see Sort Reflections on High-Cardinality Fields.
-
Click in the Partition column to select fields on which to horizontally partition the rows in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting fields on which to partition, and which partition transforms to apply to those fields, see Horizontally Partition Reflections that Have Many Rows.
If the Reflection is based on an Iceberg table, a filesystem source, an AWS Glue source, or a Hive source, and that table is partitioned, recommended partition columns and transforms are selected for you. If you change the selection of columns, then this icon appears at the top of the table:
 . You can click it to revert back to the recommended selection of partition columns.
. You can click it to revert back to the recommended selection of partition columns.
noteIgnore the Distribution column. Selecting fields in it has no effect on the Reflection.
-
-
(Optional) Optimize the number of files used to store the Reflection. You can optimize for fast refreshes or for fast read performance by queries. Follow these steps:
a. Click the
 in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.
in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.b. In the field Reflection execution strategy, select either of these options:
- Select Minimize Time Needed To Refresh if you need the Reflection to be created as fast as possible. This option can result in the data for the Reflection being stored in many small files. This is the default option.
- Select Minimize Number Of Files when you want to improve the read performance of queries against the Reflection. With this option, there tend to be fewer seeks performed for a given query.
-
Click Save when you are finished.
Edit Aggregation Reflections
You might want to edit an aggregation Reflection if you are iteratively designing and testing an aggregation Reflection, if the definition of the view that the Reflection was created from was changed, if the schema of the underlying table was changed, or if you want to revise one or more aggregations defined in the Reflection.
If you created an aggregation Reflection in the Basic view of the Reflections editor, you can edit that Reflection either in the Basic view or in the Advanced view.
Dremio runs the job or jobs to recreate the Reflection after you click Save.
Use the Basic View
To edit an aggregation Reflection in the Basic view of the Reflections editor:
-
In the Dremio console, hover over
 in the side navigation bar and select Project settings.
in the side navigation bar and select Project settings. -
Select Reflections in the project settings sidebar.
-
Click the name of the Reflection. This opens the Acceleration dialog with the Reflections editor.
-
In the Aggregation Reflection section of the editor, modify or accept the recommendation for Dimension and Measure columns.
-
Click Save.
Use the Advanced View
To edit an aggregation Reflection in the Advanced view of the Reflections editor:
-
In the Dremio console, hover over
 in the side navigation bar and select Project settings.
in the side navigation bar and select Project settings. -
Select Reflections in the project settings sidebar.
-
Click the name of the Reflection. This opens the Acceleration dialog with the Reflections editor.
-
Click the Advanced View button in the top-right corner of the editor.
-
Click Aggregation Reflections.
-
(Optional) Click in the name to rename the Reflection.
The purpose of the name is to help you understand, when you read job reports, which Reflections the query optimizer considered and chose when planning queries.
-
In the columns of the table, follow these steps, which you don't have to do in any particular order:
-
Click in the Dimension column to include or exclude fields to use as dimensions.
-
Click in the Measure column to include or exclude fields to use as measures. You can use one or more of these SQL functions for each measure:
APPROX_DISTINCT_COUNT,COUNT,MAX, andMIN.
The full list of SQL aggregation functions that Dremio supports is not supported in the Reflections editor. If you want to create a Reflection that aggregates data by using the
AVG,CORR,HLL,SUM,VAR_POP, orVAR_SAMPSQL functions, you must create a view that uses the function, and then create a raw Reflection from that view.-
Click in the Sort column to select fields on which to sort the data in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting a field on which to sort, see Sort Reflections on High-Cardinality Fields.
-
Click in the Partition column to select fields on which to horizontally partition the rows in the Reflection. For guidance in selecting fields on which to partition, and which partition transforms to apply to those fields, see Horizontally Partition Reflections that Have Many Rows.
If the Reflection is based on an Iceberg table, a filesystem source, an AWS Glue source, or a Hive source, and that table is partitioned, partition columns and transforms are recommended for you. Hover over
 at the top of the table to see the recommendation. Click the icon to accept the recommendation.
at the top of the table to see the recommendation. Click the icon to accept the recommendation.
noteIgnore the Distribution column. Selecting fields in it has no effect on the Reflection.
-
-
(Optional) Optimize the number of files used to store the Reflection. You can optimize for fast refreshes or for fast read performance by queries. Follow these steps:
a. Click the
 in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.
in the table in which you are defining the Reflection.b. In the field Reflection execution strategy, select either of these options:
- Select Minimize Time Needed To Refresh if you need the Reflection to be created as fast as possible. This option can result in the data for the Reflection being stored in many small files. This is the default option.
- Select Minimize Number Of Files when you want to improve the read performance of queries against the Reflection. With this option, there tend to be fewer seeks performed for a given query.
-
Click Save when you are finished.
External Reflections
Reference precomputed tables in external data sources instead of materializing Reflections within Dremio, eliminating refresh overhead and storage costs. You can use an external Reflection by defining a view in Dremio that matches the precomputed table and mapping the view to the external data source. The data in the precomputed table is not refreshed by Dremio. When querying the view, Dremio’s query planner leverages the external Reflection to generate optimal execution plans, improving query performance without additional storage consumption in Dremio.
Create External Reflections
To create an external Reflection:
-
Follow these steps in the data source:
a. Select your source table.
b. Create a table that is derived from the source table, such as an aggregation table, if you do not already have one.
-
Follow these steps in Dremio:
a. Define a view on the derived table in the data source. The definition must match that of the derived table.
b. Define a new external Reflection that maps the view to the derived table.
The data types and column names in the external Reflection must match those in the view that the external Reflection is mapped to.
Suppose you have a data source named mySource that is connected to Dremio. In that data source, there are (among all of your other tables) these two tables:
sales, which is a very large table of sales data.sales_by_region, which aggregates by region the data that is insales. You want to make the data insales_by_regionavailable to data analysts who use Dremio. However, because you already have thesales_by_regiontable created, you do not see the need to create a Dremio table fromsales, then create a Dremio view that duplicatessales_by_region, and finally create a Reflection on the view. You would like instead to makesales_by_regionavailable to queries run from BI tools through Dremio.
To do that, you follow these steps:
-
Create a view in Dremio that has the same definition as
Example Viewsales_by_region. Notice that theFROMclause points to thesalestable that is in your data source, not to a Dremio table.CREATE VIEW "myWorkspace"."sales_by_region" AS
SELECT
AVG(sales_amount) average_sales,
SUM(sales_amount) total_sales,
COUNT(*) sales_count,
region
FROM mySource.sales
GROUP BY region -
Create an external Reflection that maps the view above to
Example External Reflectionsales_by_regioninmySource.ALTER DATASET "myWorkspace"."sales_by_region"
CREATE EXTERNAL Reflection "external_sales_by_region"
USING "mySource"."sales_by_region"
The external Reflection lets Dremio's query planner know that there is a table in mySource that matches the Dremio view myWorkplace.sales_by_region and that can be used to satisfy queries against the view. When Dremio users query myWorkspace.sales_by_region, Dremio routes the query to the data source mySource, which runs the query against mySource.sales_by_region.
Edit External Reflections
If you have modified the DDL of a derived table in your data source, follow these steps in Dremio to update the corresponding external Reflection:
-
Replace the view with one that has a definition that matches the definition of the derived table. When you do so, the external Reflection is dropped.
-
Define a new external Reflection that maps the view to the derived table.
Test Reflections
You can test whether the Reflections that you created are used to satisfy a query without actually running the query. This practice can be helpful when the tables are very large and you want to avoid processing large queries unnecessarily.
To test whether one or more Reflections are used by a query:
-
In the Dremio console, click
 in the side navigation bar to open the SQL Runner.
in the side navigation bar to open the SQL Runner. -
In the SQL editor, type
EXPLAIN PLAN FORand then type or paste in your query. -
Click Run.
-
When the query has finished, click the Run link found directly above the query results to view the job details. Any Reflections used will be shown on the page.
View Whether Queries Used Reflections
You can view the list of jobs on the Jobs page to find out whether queries were accelerated by Reflections. The Jobs page lists the jobs that ran queries, both queries from your data consumers and queries run within the Dremio user interface.
To find whether a query used a Reflection:
-
Find the job that ran the query by looking below the details in each row.
-
Look for
 next to the job to indicate that one or more Reflections were used.
next to the job to indicate that one or more Reflections were used. -
View the job summary by clicking the row that represents the job that ran the query. The job summary appears in the pane to the right of the list of jobs.
Relationship between Reflections and Jobs
The relationship between a job and a Reflection can be one of the following types:
-
CONSIDERED – The Reflection is defined on a dataset that is used in the query but was determined not to cover the query (for example, the Reflection did not have a field that is used by the query).
-
MATCHED – A Reflection could have been used to accelerate the query, but Dremio determined that it would not provide any benefits or another Reflection was determined to be a better choice.
-
CHOSEN – A Reflection is used to accelerate the query. Note that multiple Reflections can be used to accelerate queries.
Disable Reflections
Disabled Reflections become unavailable for use by queries and will not be refreshed manually or according to their schedule.
Dremio does not disable external Reflections.
To disable a Reflection:
-
In the Dremio console, hover over
 in the side navigation bar and select Project Settings.
in the side navigation bar and select Project Settings. -
Select Reflections in the project settings sidebar.
This opens the Reflections editor for the Reflection's anchor or supporting anchor.
-
Follow one of these steps:
- If there is only one raw Reflection for the table or view, in the Basic view, click the toggle switch in the Raw Reflections bar.
- If there are two or more raw Reflections for the table or view, in the Advanced view, click the toggle switch for the individual raw Reflection that you want to disable.
- If there is only one aggregation Reflection for the table or view, in the Basic view, click the toggle switch in the Raw Reflections bar.
- If there are two or more aggregation Reflections for the table or view, in the Advanced view, click the toggle switch for the individual aggregation Reflection that you want to disable.
-
Click Save. The changes take effect immediately.
Delete Reflections
You can delete Reflections individually, or all of the Reflections on a table or view. When you delete a Reflection, its definition, data, and metadata are entirely deleted.
To delete a single raw or aggregation Reflection:
-
In the Dremio console, hover over
 in the side navigation bar and select Project settings.
in the side navigation bar and select Project settings. -
Select Reflections in the project settings sidebar.
This opens the Reflections editor for the Reflection's anchor or supporting anchor.
-
Open the Advanced view, if it is not already open.
-
If the Reflection is an aggregation Reflection, click Aggregation Reflections.
-
Click
 for the Reflection that you want to delete.
for the Reflection that you want to delete. -
Click Save. The deletion takes effect immediately.
To delete all raw and aggregation Reflections on a table or view:
-
In the Dremio console, hover over
 in the side navigation bar and select Project Settings.
in the side navigation bar and select Project Settings. -
Select Reflections in the project settings sidebar.
This opens the Reflections editor for the Reflection's anchor or supporting anchor.
-
Click the
in the top right corner of the Reflections page. -
Click Delete all reflections.
-
Click Save.
To delete an external Reflection, or to delete a raw or aggregation Reflection without using the Reflections editor, run this SQL command:
Delete a ReflectionALTER DATASET <DATASET_PATH> DROP Reflection <REFLECTION_NAME>
DATASET_PATH: The path of the view on which the external Reflection is based.REFLECTION_NAME: The name of the external Reflection.
Related Topics
- Data Reflections Deep Dive – Enroll in this Dremio University course to learn more about Reflections.
- Operational Excellence - Follow best practices in Dremio's Well-Architected Framework for creating and managing Reflections.