Jobs
All jobs run in Dremio are listed on a separate page, showing the job ID, type, status, and other attributes.
To navigate to the Jobs page, click ![]() in the side navigation bar.
in the side navigation bar.
Search Filters and Columns
By default, the Jobs page lists the jobs run within the last 7 days and the jobs are filtered by UI, External Tools job types. To change these defaults for your account, you can filter on values and manage columns directly on the Jobs page, as shown in this image:
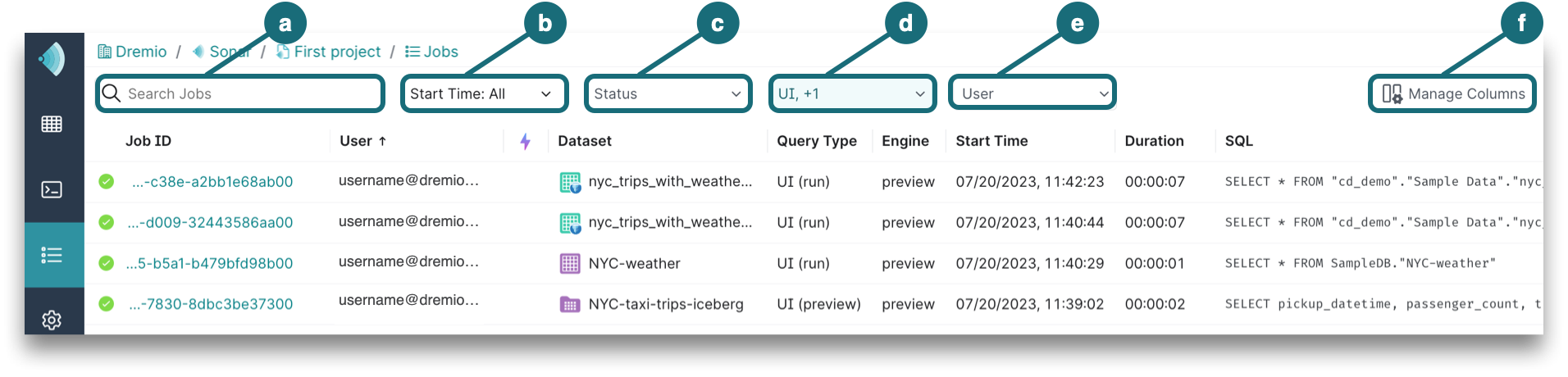
a. Search Jobs by typing the username or job ID.
b. Start Time allows you to pick the date and time at which the job began.
c. Status represents one or more job states. For descriptions, see Job States and Statuses.
d. Attribute includes Accelerator, AI agent, AI function, Downloads, External Tools, Internal, MCP, and UI. For descriptions, see Job Properties.
e. User can be searched by typing the username or checking the box next to the username in the dropdown.
f. Manage Columns by checking the boxes next to additional columns that you want to see in the Jobs list. The grayed out checkboxes show the columns that are required by default. You can also rearrange the column order by clicking directly on a column to drag and drop.
Job Properties
Each job has the following properties, which can appear as columns in the list of jobs on the Jobs page or as details on the Job Details page:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Accelerated | A purple lightning bolt in a row indicates that the job ran a query that was accelerated by one or more Reflections. |
| Query Type | Represents one of the following query types:
|
| CPU Used | Provides statistics about the actual cost of the query operations in terms of CPU processing. |
| Dataset | The queried dataset, if one was queried. Hover over the dataset to see a metadata card appear with details about the dataset. For more information, see Discover Data. |
| Duration | The length of time (in seconds) that a job required from start to completion. |
| Engine | The engine used to run the query. |
| Input | The number of bytes and the number of rows considered for the job. |
| Job ID | A universally unique identifier. |
| Output | The number of bytes and the number of rows resulted as output from the job. |
| Planner Cost Estimate | A cost estimate calculated by Dremio based on an evaluation of the resources that to be used in the execution of a query. The number is not in units, and is intended to give a an idea of the cost of executing a query relative to the costs of executing other queries. Values are derived by adding weighted estimates of required I/O, memory, and CPU load. In reported values, K = thousand, M = million, B = billion, and T = trillion. For example, a value of 12,543,765,321 is reported as 12.5B. |
| Planning Time | The length of time (in seconds) in which the query optimizer planned the execution of the query. |
| Rows Returned | Number of output records. |
| Rows Scanned | Number of input records. |
| SQL | The SQL query that was submitted for the job. |
| Start Time | The date and time which the job began. |
| Status | Represents one or more job states. For descriptions, see Job States and Statuses. |
| Total Memory | Provides statistics about the actual cost of the query operations in terms of memory. |
| User | Username of the user who ran the query and initiated the job. |
| Wait on Client | The length of time (in seconds) that is waiting on the client. |
Job States and Statuses
Each job passes through a sequence of states until it is complete, though the sequence can be interrupted if a query is canceled or if there is an error during a state. In this diagram, the states that a job passes through are in white, and the possible end states are in dark gray.
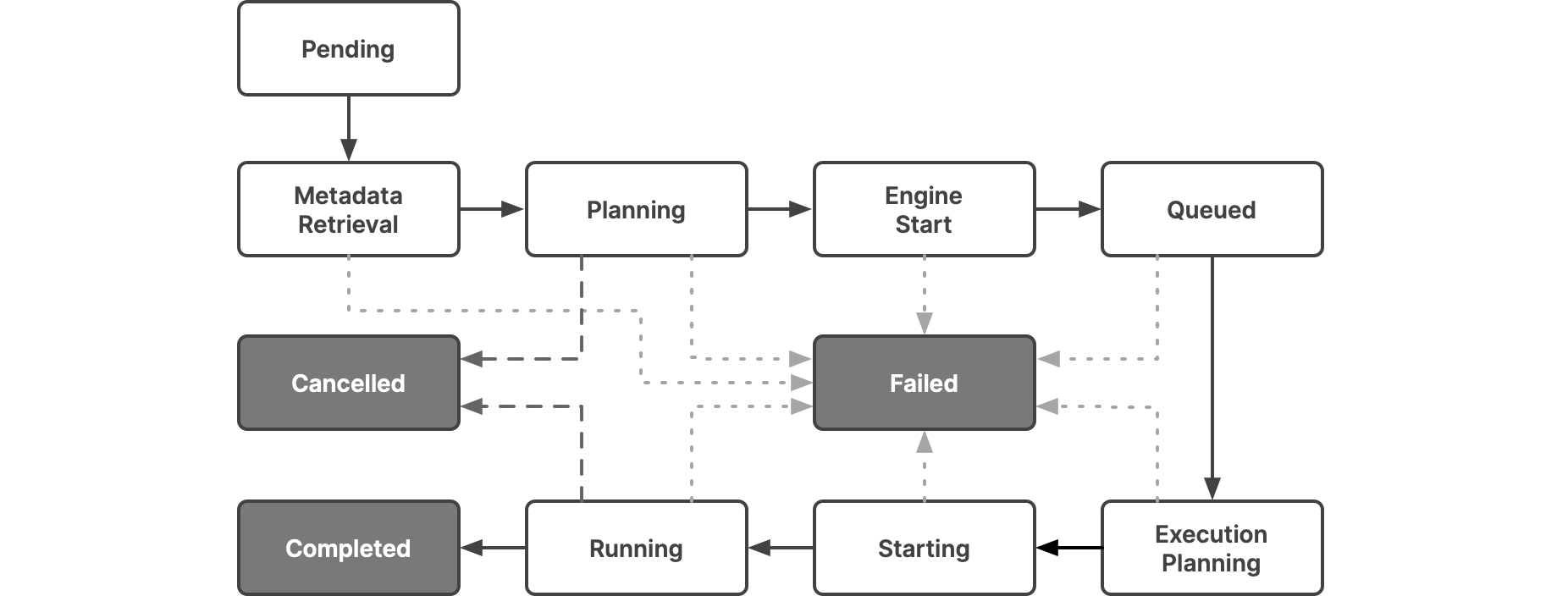
This table lists the statuses that the UI lets you filter on and shows how they map to the states:
| Icon | Status | State | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup | Pending | Represents a state where the query is waiting to be scheduled on the query pool. | |
| Metadata Retrieval | Represents a state where metadata schema is retrieved and the SQL command is parsed. | ||
| Planning | Represents a state where the following are done:
| ||
| Engine Start | Engine Start | Represents a state where the engine starts if it has stopped. If the engine is stopped, it takes time to restart for the executors to be active. If the engine is already started, then this state does not have a duration. | |
| Queued | Queued | Represents a state where a job is queued. Each engine has a limit of concurrent queries. If the queries in progress exceed the concurrency limit, the query should wait until the jobs in progress complete. | |
| Running | Execution Planning | Represents a state where executor nodes are selected from the chosen engine to run the query, and work is distributed to each executor. | |
| Running | Represents a state where executor nodes execute and complete the fragments assigned to them. Typically, most queries spend more time in this state. | ||
| Starting | Represents a state where the query is starting up. | ||
| Canceled | Canceled | Represents a terminal state that indicates that the query is canceled by the user or an intervention in the system. | |
| Completed | Completed | Represents a terminal state that indicates that the query is successfully completed. | |
| Failed | Failed | Represents a terminal state that indicates that the query has failed due to an error. |
View Job Details
You can view the details of a specific job by viewing the Overview, SQL, Visual Profile, and Raw Profile tabs on the Job Details page.
To navigate to the job details:
- Click
 in the side navigation bar.
in the side navigation bar. - On the Jobs page, click a job for which you would like to view the details.
- The Job Details page then replaces the list of jobs.
Explain SQL
Use the Explain SQL option in the SQL Runner to analyze and optimize your SQL queries with assistance from the AI Agent. In the SQL Runner, highlight the SQL you want to review, right-click, and select Explain SQL. This prompts the AI Agent to examine the query, datasets, and underlying architecture to identify potential optimizations. The AI Agent uses Dremio’s SQL Parser—the same logic used during query execution—to identify referenced tables, schemas, and relationships. Based on this analysis, the Agent provides insights and recommendations to improve query performance and structure. You can continue interacting with the AI Agent to refine the analysis and iterate on the SQL. The AI Agent applies SQL best practices when suggesting improvements and may execute revised queries to validate quality before presenting recommendations.
Explain Job
Use the Explain Job option on the Job Details page to analyze job performance and identify opportunities for optimization. From the Job Details page, click Explain Job to prompt the AI Agent to review the job’s query profile, planning, and execution details to compare with the AI Agent’s internal understanding of optimal performance characteristics. The AI Agent generates a detailed analysis that highlights key performance metrics such as data skew, memory usage, threading efficiency, and network utilization. Based on this assessment, it recommends potential optimizations to improve performance and resource utilization. You can continue the conversation with the AI Agent to explore the job in greater depth or reference additional job IDs to extend the investigation and compare results.
The main components of the Job Details page are numbered below:
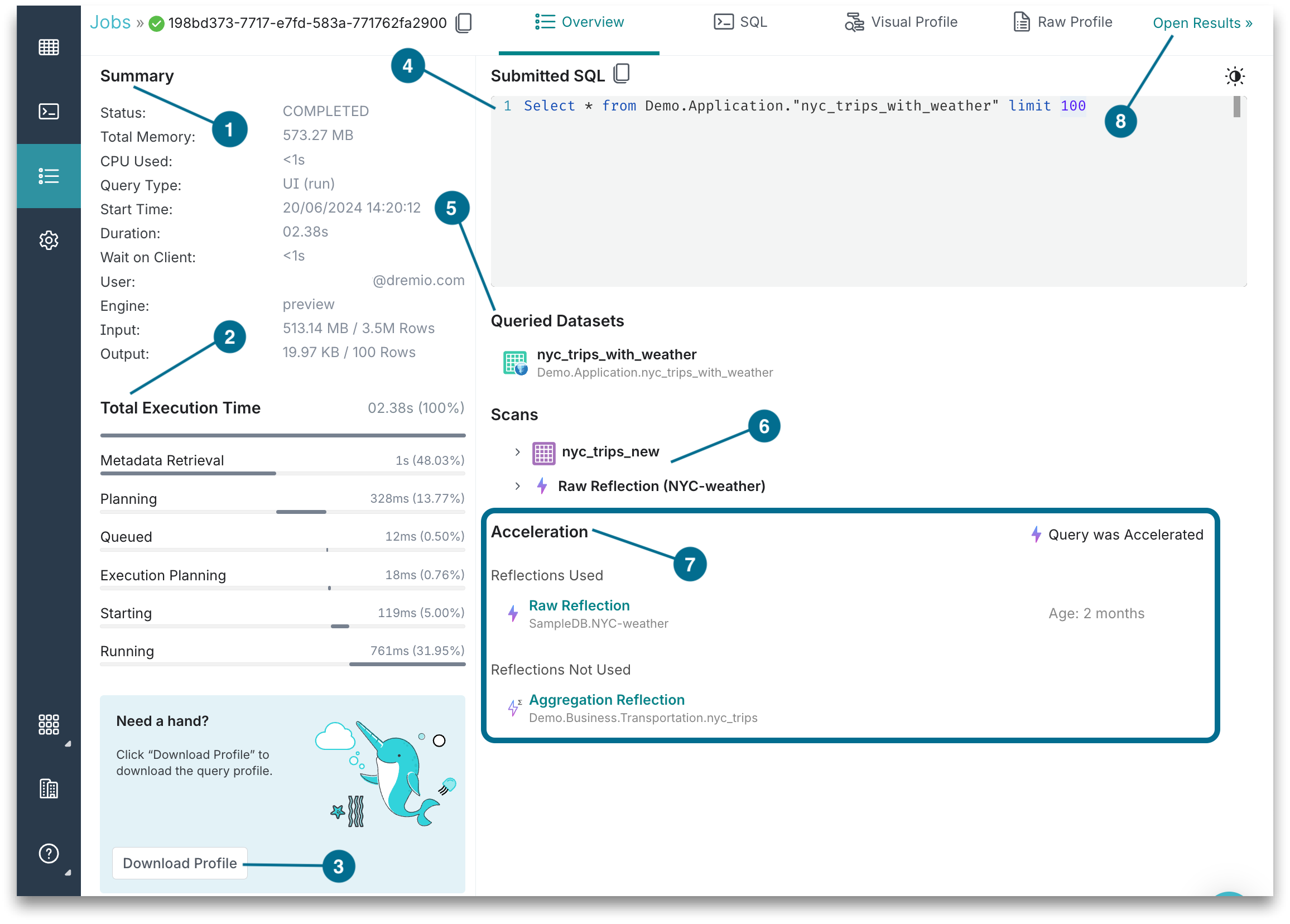
1. Summary
Each job is summarized.
2. Total Execution Time
The total execution time is the length of time for the total execution and the job state durations in the order they occur. Only the duration of the Engine Start state is in minutes and seconds. If the engine is stopped, it takes time to restart for the executors to be active. If the engine is already started, then Engine Start duration does not have a value. For descriptions, see Job States and Statuses.
3. Download Profile
To download the query profile, click the Download Profile button in the bottom-left corner of the Overview tab on the Job Details page. The profile will help you see more granular details about the job.
The profile downloads as a ZIP file. When you extract the ZIP file, you will see the following JSON files:
- profile_attempt_0.json: This file helps with troubleshooting out of memory and wrong results issues. Note that the start and end time of the query is provided in EPOCH format. See the Epoch Converter utility for converting query time.
- header.json: This file provides the full list of Dremio coordinators and executors, data sets, and sources. This information is useful when you are using REST calls.
4. Submitted SQL
The SQL query for the selected job.
5. Queried Datasets
The datasets queried for the selected job. These can be views or tables.
6. Scans
Scan details include the source type, scan thread count, IO wait time (in milliseconds), and the number of rows scanned.
7. Acceleration
Only if the job was accelerated, the Acceleration section appears and Reflections data is provided. See Optimize Performance for more information.
8. Results
To see the job results, click the Open Results link in the top-right corner of the Job Details page. As long as the engine that ran the job is up, the Open Results link is visible in the UI. It disappears when the engine that ran the job shuts down and is only visible for the jobs that are run through the UI.
Job SQL
Next to the Job Details page is the SQL tab, which shows the Submitted SQL and Dataset Graph.
You can view the SQL statement that was used for the selected job. Although the SQL statement is in read-only mode on the SQL Details page, the statement can be copied from the page and pasted into the SQL editor.
A dataset graph only appears if there is a queried dataset for the selected job. The dataset graph is a visual representation of the datasets used in the SQL statement.
Related Topics
- Profiles – See the visual profiles and raw profiles of jobs.