Formatting Data to a Table
After configuring your data source, you can create a table using the data from an individual file or a folder of files in your source and then query the table using SQL in Dremio. You can query the file or folder without creating a table, but performance may be impacted.
This functionality is currently only supported on Object Storage sources.
Supported File Formats
- Apache Iceberg
- Delta Lake
- Excel
- JSON
- Parquet
- Text (delimited)
- XLS
- Formatting folders that contain a mix of file formats is not supported. All files in a folder must be the same format.
- The names of files and folders cannot include the following special characters:
/,:,[, or]. - Formatting CSV files that are encoded in UTF-16 is not supported.
- Dremio can read delimited text files and JSON files that are compressed in GZIP (
.gz) files. You can promote such files just as you would promote non-compressed ones. Dremio does not recognize file formats automatically when files are compressed, so you must select the format manually when promoting.
Formatting a File or Folder as a Table
To format a file or folder as a table:
-
On the Datasets page, navigate to the file or folder that you want to format.
-
To format a file or folder:
File: Hover over the file to format and click
 on the far right.
on the far right.Folder: Hover over the folder to format and click
 on the far right.
on the far right. -
In the Dataset Settings dialog, for Format, verify that the correct format has been detected.
-
(Optional) For the Parquet format, click the checkbox to enable the Ignore other file formats if desired. If you select this option, Dremio ignores all non-Parquet files in the related folder structure, and the promoted table works as if only Parquet files are in the folder structure.
-
(Optional) For Excel, XLS, and Text (delimited) formats, you can configure the following parameters.
Excel and XLS format:
Parameter Description Extract Field Names Check this box to extract the column names from the first line of the file. Expand Merged Cells Check this box to expand out cells that have been merged in the Excel sheet. Sheet Name Specify the sheet name if there are multiple sheets within the file. Text (delimited) format:
Parameter Description Field Delimiter Select the delimiter in your text file - Comma, Tab, Pipe, or Custom. For Custom, enter the characters used for a delimiter in the text box. Quote Select the character that is used for quotes in your file - Single Quote, Double Quote, Custom. For Custom, enter the characters used for quotes in the text box. Comment Select the character that is used for comments in your file - Number Sign, Double Slash, Custom. For Custom, enter the characters used for comments in the text box. Line Delimiter Select the character that is used for a line delimiter in your file - CRLF, LF, Custom. For Custom, enter the characters used for a line delimiter in the text box. Escape Select the character that is used for to escape in your file - Double Quote, Back Quote, Backslack, Custom. For Custom, enter the characters used to escape in the text box. Extract Field Names Select this option to extract the column names from the first line of the file. Skip First Line Select this option to skip the first line of the file. Trim Column Names Select this option to trim whitespace from the left and right sides of the names of the columns. This option is checked by default. -
Click Save. The parameter values will be auto-detected but can be altered. When you click Save, a purple icon will be next to your dataset to represent it as a table on the Datasets page. Tables created from a folder of files display as a folder
 , whereas tables created from a single file are represented by a grid
, whereas tables created from a single file are represented by a grid  .
.
Partitioned Data
The data in a source dataset might be partitioned into one or more levels of subfolders, one level for each partition column. In such cases, when you format the source dataset as a table, Dremio appends to the table one column per partition. The data type of the appended columns is varchar.
Examples
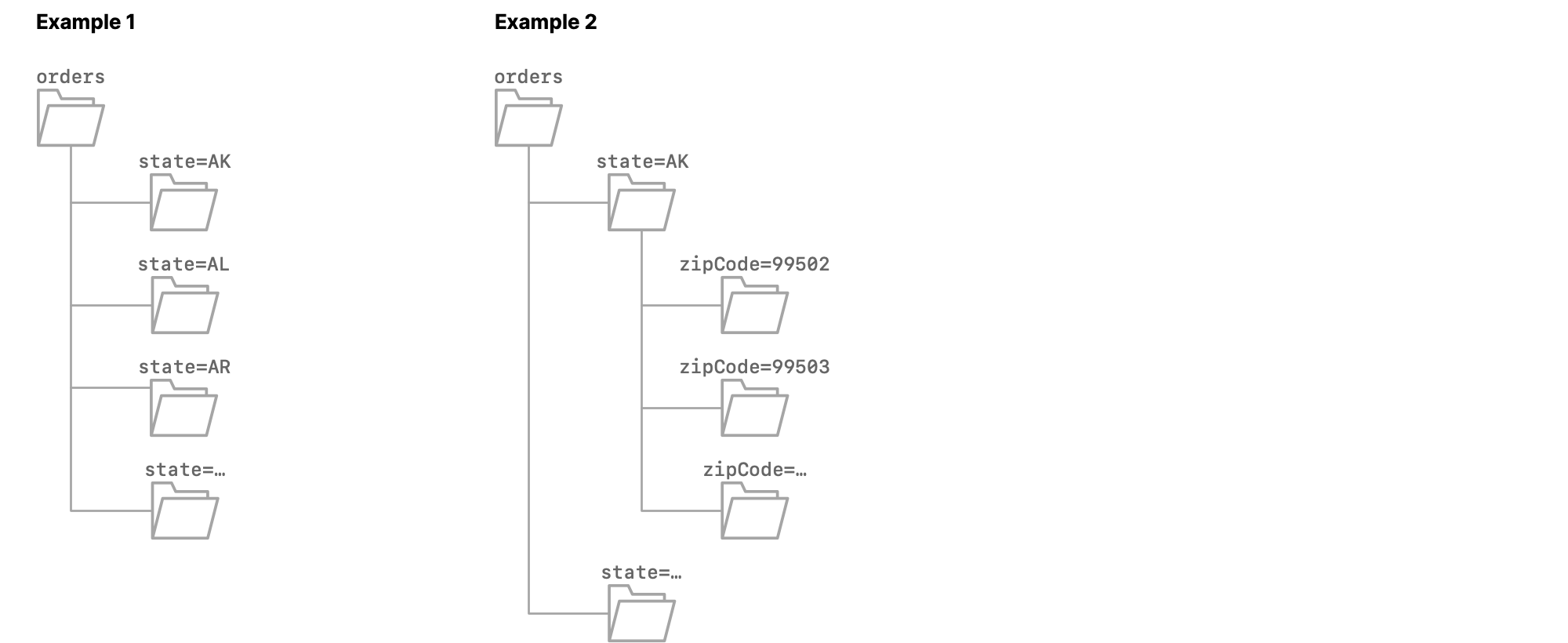
Example 1
The source dataset orders is partitioned on the column state. Each subfolder is named state=<abbreviation>, where <abbreviation> is the two-letter abbreviation of the name of a US state.
When you format orders as a table, all of the columns from the Parquet files, except state, are included, and Dremio appends the column dir0, which has the data type varchar. The values in that column are state=AK for the rows from the file 0.parquet, state=AL for the rows from the file 1.parquet, state=AR for the rows from the file 2.parquet, and so on.
Example 2
The source dataset orders is partitioned on the columns state and zipCode. Each first-level subfolder is named state=<abbreviation>, where <abbreviation> is the two-letter abbreviation of the name of a US state. Each second-level subfolder is named zipCode=<zip code>.
When you format orders as a table, all of the columns from the Parquet files, except state and zipCode, are included, and Dremio appends the columns dir0 and dir1, which both have the data type varchar.
The values in dir0 are state=AK for all rows in which the value in dir1 is zipCode=<zip code in AK>, state=AL for all rows in which the value in dir1 is zipCode=<zip code in Al>, and so on.
The values in dir1 are zipCode=99502 for the rows from 0.parquet, zipCode=99503 for the rows from 1.parquet, and so on.
Partition Column Inference
By default, when a source dataset uses Parquet files and the data is partitioned on one or more columns, Dremio behaves as described in Partitioned Data. However, if you select the option Enable partition column inference in the advanced options for a data source, you change how Dremio handles partition columns.
In addition to appending a column named dir<n> for each partition level and using subfolder names for values in those columns, Dremio detects the name of the partition column, appends a column that uses that name, detects values in the names of subfolders, and uses those values in the appended column.
Appended columns still use the varchar data type.
Examples
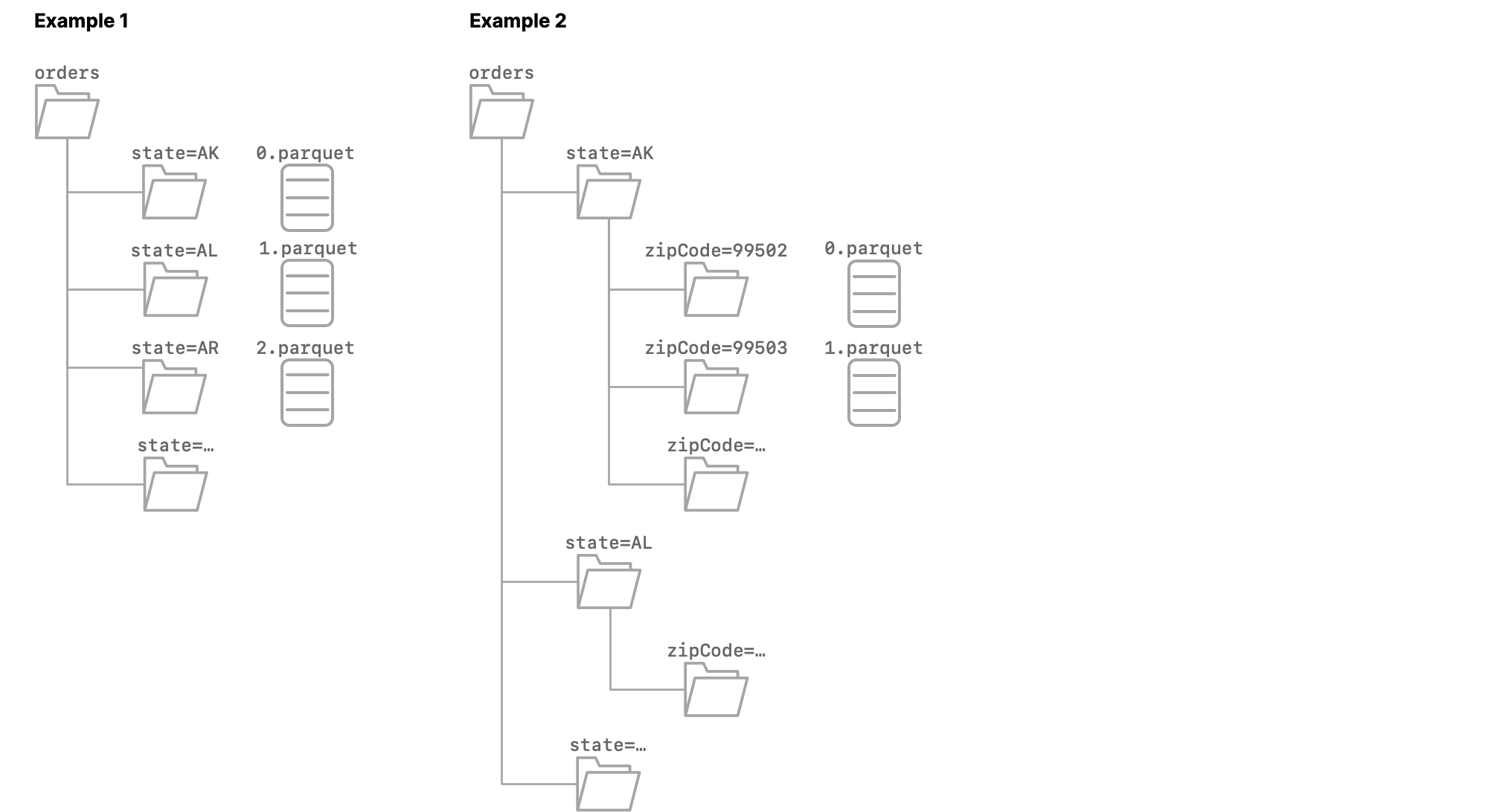
Example 1
The source dataset orders is partitioned on the column state. Each subfolder is named state=<abbreviation>, where <abbreviation> is the two-letter abbreviation of the name of a US state.
When you format orders as a table, all of the columns from the Parquet files are included, and Dremio appends the columns dir0 and state, both of which use the varchar data type.
The values in dir0 are state=AK for the rows from the file 0.parquet, state=AL for the rows from the file 1.parquet, state=AR for the rows from the file 2.parquet, and so on.
The values in state are AK for the rows from the file 0.parquet, AL for the rows from the file 1.parquet, AR for the rows from the file 2.parquet, and so on.
Example 2
The source dataset orders is partitioned on the columns state and zipCode. Each first-level subfolder is named state=<abbreviation>, where <abbreviation> is the two-letter abbreviation of the name of a US state. Each second-level subfolder is named zipCode=<zip code>.
When you format orders as a table, all of the columns from the Parquet files are included, and Dremio appends the columns dir0, dir1, state, and zipCode, all of which use the varchar data type.
The values in dir0 are state=AK for all rows in which the value in dir1 is zipCode=<zip code in AK>, state=AL for all rows in which the value in dir1 is zipCode=<zip code in Al>, and so on.
The values in dir1 are zipCode=99502 for the rows from 0.parquet, zipCode=99503 for the rows from 1.parquet, and so on.
The values in state are AK for all rows in which the value in zipCode is <zip code in AK>, AL for all rows in which the value in zipCode is <zip code in Al>, and so on.
The values in zipCode are 99502 for the rows from 0.parquet, 99503 for the rows from 1.parquet, and so on.
Requirements
For the Enable partition column inference option to work correctly, ensure that the names of your subfolders meet these requirements:
-
Names must be in the format
column_name=<column_value>.colum_name=is a valid input. -
Names must meet Dremio's naming conventions for columns.
-
Names must be unique within and across directory levels.
-
Names must not be present in data files.
-
All Parquet files in the source dataset must be in leaf subfolders.
How Dremio Handles Existing Tables
If you enable the Enable partition column inference option, and already have one or more tables that are based on sources that use Parquet files and that are partitioned, those existing tables remain as they are until you run the ALTER command twice on each. The first time, you run the command to cause Dremio to forget the metadata for the table. The second time, you run the command to cause Dremio to refresh the metadata. The commands are listed here on each of those tables.
For example, before you enable the Enable partition column inference option, your orders table might have these columns:
| orderID | multiple columns | dir0 |
|---|---|---|
| 000001 | ... | state=CA |
| 000002 | ... | state=WA |
Suppose that you enable the Enable partition column inference option. The columns in the table remain the same. If you want to take advantage of partition column inference, you run these two SQL commands:
SQL commands for partition column inferenceALTER TABLE path.to.orders FORGET METADATA
ALTER TABLE path.to.orders REFRESH METADATA
As a result of the second ALTER command, Dremio adds the column state:
| orderID | multiple columns | dir0 | state |
|---|---|---|---|
| 000001 | ... | state=CA | CA |
| 000002 | ... | state=WA | WA |
Because Dremio appends the new column, any views that are defined on the table and that use the dir0 column are still valid. When you define new views, you can use the appended column.
Enabling Partition Column Inference
After you follow the steps in either of these procedures, Dremio uses partition column inference for all source datasets that you format to tables.
To enable partition column inference for a new source:
- On the Datasets page, click Add Source below the list of sources.
- Select Advanced Options.
- Select Enable partition column inference.
- Specify any other settings that you want for your new data source.
- Click Save.
To enable partition column inference for an existing source:
- On the Datasets page, click the name of the data source.
- In the top-right corner of the page, click
 .
. - In the Edit Source dialog, select Advanced Options.
- Select Enable partition column inference.
- Click Save.
- If there are existing tables that are based on datasets in the current data source, run the two ALTER commands described here on each of those tables.
If you change the partitioning schema of a source dataset after enabling partition column inference, metadata refreshes of all tables defined on the source dataset fail. To resolve this problem, run the two ALTER commands described here on each of the affected tables.
ALTER Commands to Cause Dremio to Forget and to Refresh Metadata
When you enable partition column inference on a source, you might have one or more existing tables in Dremio that are based on datasets in that source. Also, you might you enable partition column inference on a source and then change the partition schema of a source dataset that is the basis of one or more tables in Dremio.
In both cases, you must run these two ALTER commands on each affected table:
SQL ALTER commands to forget and refresh metadataALTER TABLE <dataset_path> FORGET METADATA
ALTER TABLE <dataset_path> REFRESH METADATA
Enabling Automatic Formatting of Data
You can configure a source to automatically format the data located in the source to tables when a user triggers a query on the data for the first time.
To configure data to be automatically formatted:
- Click on the Object Storage header in the left panel on the Datasets page.
- On the Object storage page, hover over the source for which you want to enable this property. Click
 on the far right and select Settings.
on the far right and select Settings. - In the Source Settings dialog, select Metadata from the source settings sidebar.
- On the Metadata tab, click the checkbox to Automatically format files into tables when users issue queries.
- Click Save.
Removing Formatting on Data
Removing the formatting on a table will revert the table to the folder or file format that it was originally in.
To remove the formatting on data:
- On the Datasets page, locate the table for which you want to remove formatting.
- Hover over the table for which you want to remove formatting. Click
 and select Remove Format.
and select Remove Format. - In the Remove Format dialog, confirm that you want to remove formatting for the selected dataset. Any views that have been created from this table will be disconnected from the parent.