Key Concepts
This page contains definitions for key Dremio concepts.
Tables and Views
A table contains the data from your source, formatted as rows and columns. Tables can be created in your catalog or they can be formatted from a folder or file in a source. Tables created from a folder of files display as a folder ![]() , whereas tables created from a single file are represented by a grid
, whereas tables created from a single file are represented by a grid ![]() .
.
You can create view, which are derived from tables or other views. Views are defined by the steps necessary for their creation, including transformations, filters, joins, and other modifications. Views are logical representations of data so they use very little memory and always reflect the current state of the parent tables or views they are derived from. A view is represented by .
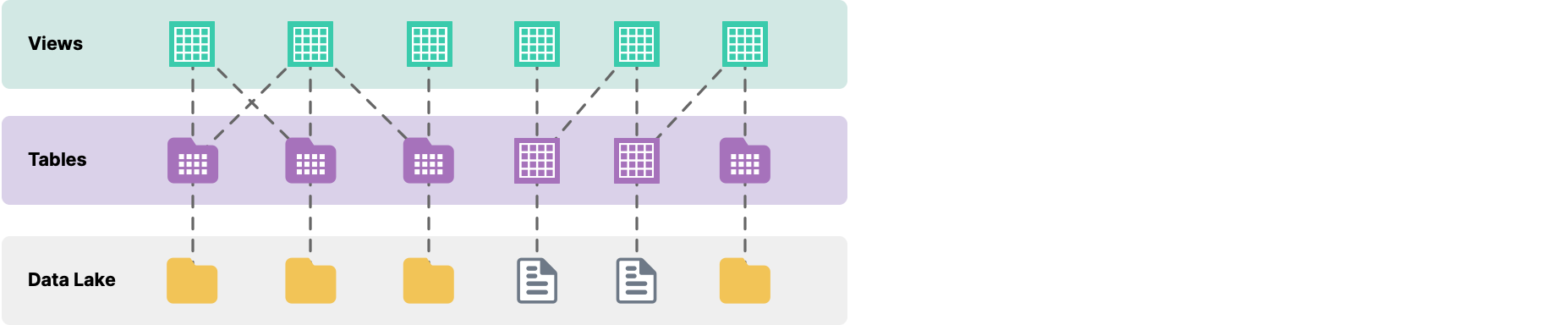
Let's imagine a dataset is represented as a sales table. We can open this dataset within Dremio, and save it as a view called salesRaw. Later on we can derive another view called salesNY from salesRaw by excluding all data that doesn't originate from the state of New York. salesRaw and salesNY can each be queried and will return different results, but they are both based on the same underlying table.
Reflections
A Reflection (either autonomous or manual) in Dremio is a precomputed, optimized copy of source data or query results that accelerates query performance by allowing the system to avoid scanning original data. When processing a query, Dremio automatically identifies any relevant Reflections, evaluates whether they can satisfy the query requirements, and compares Reflection-based approaches against direct table access to select the lowest-cost execution plan. The query optimizer then transparently rewrites queries to use Reflections when beneficial, typically resulting in less expensive execution plans without requiring users to reference Reflections directly.
For more information, see Reflections.
Spaces and Folders
A space is a top-level folder that is used to group views by common themes such as a project, purpose, department, or geographic region.
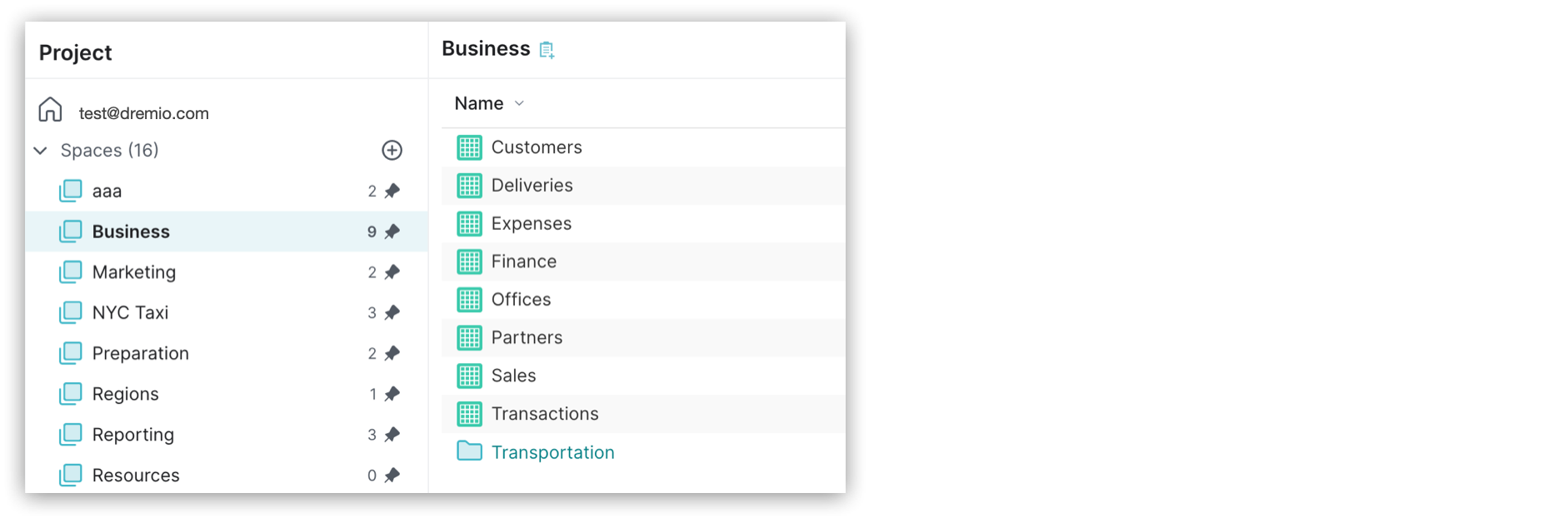
Spaces can be further organized by creating a hierarchy of folders. Folders can contain other folders, and they are represented by .
To reference a view that is in a folder or subfolder, use the dot-separated path to the location of view. For example, in the sales.transactions.north_america.sales_new_york path, sales is the name of the space, transactions and north_america are folders within the space, and sales_new_york is the view name.
Home Space
Each user has a home space that can be used to upload local files or experimentation. A user's home space and the contents of it are private to the user by default. To view your home space, click ![]() and your username in the Data panel.
and your username in the Data panel.